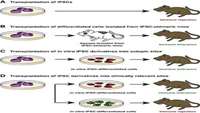
Molecular Obstacles to Clinical Translation of iPSCs
The ability to reprogram somatic cells into induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) using defined factors provides new tools for biomedical research. However, some iPSC clones display tumorigenic and immunogenic potential, thus raising concerns about their utility and safety in the clinical setting.
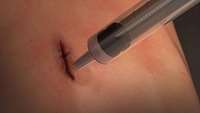
Research directed by Iranian scientists resulted in: development of elastic surgical glue that seals wounds in 60 seconds
A research team supervised by “Nasim Annabi”, Iranian scientist and assistant professor of Northeastern University and a researcher affiliated to Harvard Medical School and Harvard-MIT Division of Health Sciences and Technology, and “Ali Khademhosseini”, Iranian professor at Harvard Medical School and Harvard-MIT Division of Health Sciences and Technology, has successfully developed an elastic surgical glue that can sealing up critical wounds in the skin or the organs, in 60 seconds, without the need for staples or sutures.
Business Activity in the Field: what are companies doing and why?
The REGenableMED project work-package on business models, value chains and innovation ecosystems investigated 10 UK case studies composed of 7 private firms, 1 public organisation, 1 university spin off and 1 research and development consortium.
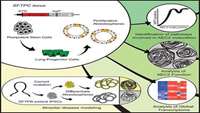
Differentiation of Human Pluripotent Stem Cells into Functional Lung Alveolar Epithelial Cells
Lung alveoli, which are unique to air-breathing organisms, have been challenging to generate from pluripotent stem cells (PSCs) in part because there are limited model systems available to provide the necessary developmental roadmaps for in vitro differentiation
Overcoming Challenges Facing Advanced Therapies in the EU Market
Recent developments in therapeutic technologies have enabled a much-needed shift from classical “one size fits all” protocols to personalized medicine strategies.
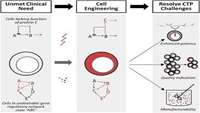
Achieving Efficient Manufacturing and Quality Assurance through Synthetic Cell Therapy Design
New methods to manipulate gene and cell state can be used to engineer cell functionality, simplify quality assessment, and enhance manufacturability. These strategies could help overcome unresolved cell therapy manufacturing challenges and complement frameworks to design quality into these complex cellular systems, ultimately increasing patient access to living therapeutics.
Plant substance shows inhibitory effects on cancer stem cells
The plant Ambrosia arborescens grows at a high elevation in large parts of South America, and is traditionally used as a medicinal plant. The researchers have isolated the sesquiterpene lactone damsin from the plant and studied its effect on cancer stem cells in three different breast cancer cell lines.
DNA surgery on embryos removes disease
The team at Sun Yat-sen University used a technique called base editing to correct a single error out of the three billion "letters" of our genetic code.
Beta Cell Replacement in Mice Using Human Type 1 Diabetes Nuclear Transfer Embryonic Stem Cells
Beta cells derived from stem cells hold great promise for cell replacement therapy for diabetes. Here we examine the ability of nuclear transfer embryonic stem cells (NT-ES) derived from a type 1 diabetes patient to differentiate into beta cells, and provide a source of autologous islets for cell replacement
Regenerative cardiac drug receives federal funding
Novo Biosciences Inc., a spinoff of the MDI Biological Laboratory (both ME, USA), has announced that it has received a 2 year, US$1.5 million Small Business Innovation Research (SBIR) grant from the National Institutes of Health (NIH) for the development of MSI-1436 as a potential regenerative medicine therapy for the treatment of patients who have suffered an acute heart attack.