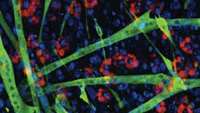
Breast cancer cells in mice tricked into turning into fat cells
As cancer cells respond to cues in their microenvironment, they can enter a highly plastic state in which they are susceptible to transdifferentiation into a different type of cell. Researchers at the University of Basel in Switzerland exploited this critical phase, known as an epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT), to coax breast cancer cells in mice to turn into harmless fat cells. The proof-of-concept study appears January 14 in the journal Cancer Cell.
Transplanted bone marrow endothelial progenitor cells delay ALS disease progression
Transplantation of human bone marrow-derived endothelial progenitor cells (EPCs) into mice mimicking symptoms of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) helped more motor neurons survive and slowed disease progression by repairing damage to the blood-spinal cord barrier (BSCB), University of South Florida researchers report.
New approach to drug discovery could lead to personalized treatment of neuropsychiatric disorders
Researchers have developed a method that could drastically accelerate the search for new drugs to treat mental health disorders such as schizophrenia.
Grails multi-cancer blood test expands data in over 20 disease types
Grail has taken a few more steps forward in its quest to develop a diagnostic test capable not only of spotting cancer in its earliest stages, but also identifying its location within the body using markers taken from the bloodstream.
World first as artificial neurons developed to cure chronic diseases
Artificial neurons on silicon chips that behave just like the real thing have been invented by scientists – a first-of-its-kind achievement with enormous scope for medical devices to cure chronic diseases, such as heart failure, Alzheimer’s, and other diseases of neuronal degeneration.
CARVER: CRISPR–Cas13 system kills viruses in human cells
Researchers at the Broad Institute of MIT and Harvard (both MA, USA) have designed a Cas13–CRISPR construct that can act as a diagnostic and antiviral. The ‘CARVER’ system, detailed in Molecular Cell, offers promise for tackling emerging and drug-resistant RNA viruses.
Osteoblastic cell stimulation by pulsed electromagnetic fields
Bone fracture healing can be augmented with the application of pulsed electromagnetic fields (PEMFs), but a consensus regarding idealized conditions is lacking. A new study characterizes the in vitro effects of these PEMFs on the crucial osteoblast precursor cells and seeks to determine the optimal conditions that will promote bone regeneration.
Adipogenic progenitors keep muscle stem cells young
In adult skeletal muscle, loss of myofiber integrity caused by mechanical injuries or diseases are repaired by resident muscle stem cells, called satellite cells, which promptly exit from quiescence after disruption of muscle architecture to expand, differentiate and drive tissue regeneration.
New polymer heart valve implanted in first patient
Caltech researchers have helped to design a new generation of heart valves that are longer-lasting, cost less to manufacture, and are more biocompatible than options that are currently available to patients. As part of an FDA trial, one of the new valves was implanted into a human for the first time in late July.
An advance for drug-eluting contact lenses: Delivery to the back of the eye
Drug-eluting contact lenses, which gradually release drugs into the eye, offer a promising alternative to daily eye drops, which can be unpleasant and hard for patients to properly administer.