Development of a Chimeric Model to Study and Manipulate Human Microglia In Vivo
iPSC-derived microglia offer a powerful tool to study microglial homeostasis and disease-associated inflammatory responses. Yet, microglia are highly sensitive to their environment, exhibiting transcriptomic deficiencies when kept in isolation from the brain.
Scientists identify method to study resilience to pain
Scientists at the Yale School of Medicine and Veterans Affairs Connecticut Healthcare System have successfully demonstrated that it is possible to pinpoint genes that contribute to inter-individual differences in pain.
Discovery of the genetic conductor of brain stem cells
Our brain comprises 85 billion nerve cells and just as many so-called glial cells, which work in close contact with the former to guarantee their proper function.
FRESH 3D Printing Used to Rebuild Functional Components of the Human Heart
Scientists have taken a major step closer to being able to 3D bioprint functional organs, after researchers devised a method of rebuilding components of the human heart, according to a study published in the August 2nd edition of Science.
Scientists Have Built Synthetic Cells That React to External Cues, Just Like Real Ones
Researchers have developed artificial cells that can respond to external chemical forces, just like real ones do. This exciting step could get us closer to using synthetic biological structures in real-world situations, such as targeted drug delivery or cleaning up pollution.
Meet the xenobot: worlds first living, self-healing robots created from frog stem cells
Scientists have created the worlds first living, self-healing robots using stem cells from frogs.
Embryos early development revealed in a dish
During embryonic development, the entire nervous system, the skin and the sensory organs emerge from a single sheet of cells known as the ectoderm. While there have been extensive studies of how this sheet forms all these derivatives, it hasnt been possible to study the process in humans until now.
Plant-based compound may enable faster, more effective gene therapy
Gene therapy has broadened the treatment possibilities for those with immune system deficiencies and blood-based conditions, such as sickle cell anemia and leukemia. These diseases, which once would require a bone marrow transplant, can now be successfully treated by modifying patients own blood stem cells to correct the underlying genetic problem.
Early mouse fetuses generated without sperm or eggs for first time
For the first time, artificial embryos made without sperm or eggs have started to form live fetuses after being implanted in female mice. However, the embryos had some malformations and we are still a long way from being able to make human babies this way.
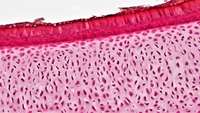
Humans have salamander-like ability to regrow cartilage in joints
Contrary to popular belief, cartilage in human joints can repair itself through a process similar to that used by creatures such as salamanders and zebrafish to regenerate limbs, researchers at Duke Health found.