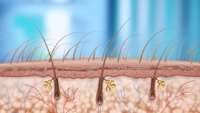
Researchers identify microRNA that shows promise for hair regrowth
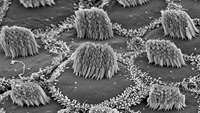
Researchers from North Carolina State University have identified a microRNA (miRNA) that could promote hair regeneration. This miRNA—miR-218-5p—plays an important role in regulating the pathway involved in follicle regeneration, and could be a candidate for future drug development.
Lego-inspired bone and soft tissue repair with tiny, 3D-printed bricks
Tiny, 3-D-printed bricks have been designed to heal broken bones—and could one day lead to lab-made organs for human transplant.
Fat cell hormone enhances therapeutic potential of MSC therapy
Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) have the potential to differentiate into a range of different cell types, including bone, fat, and muscle cells. But it's their ability to stimulate the repair of damaged tissue that has captured the interest of researchers worldwide, with MSCs demonstrating therapeutic effects in the treatment of conditions such as heart disease, liver cirrhosis, and diabetes.
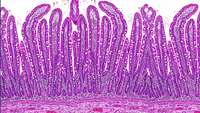
How to repair your gut
In a world first, Monash University researchers have identified a key biomolecule that enhances the repair of your gut lining by prompting stem cells to regenerate damaged tissue.
Not Just Stem Cells: The Potential in Umbilical Cord Exosomes
Exosomes, the small—normally only 30–100 nano-meters across—extracellular vesicles released from cells are not only carriers of cellular waste, as once believed, but also now known to facilitate cellular functions important to survival such as cell-to-cell communication and immunological responses.
Scientists find a simpler way to make sensory hearing cells
Scientists from the USC Stem Cell laboratories of Neil Segil and Justin Ichida are whispering the secrets of a simpler way to generate the sensory cells of the inner ear. Their approach uses direct reprogramming to produce sensory cells known as "hair cells," due to their hair-like protrusions that sense sound waves. The study was published today in the journal eLife.
Gut microbiome influences ALS outcomes
Harvard University scientists have identified a new gut-brain connection in the neurodegenerative disease amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, or ALS. The researchers found that in mice with a common ALS genetic mutation, changing the gut microbiome using antibiotics or fecal transplants could prevent or improve disease symptoms.
Antidepressant harms developing neurons in lab-grown 'mini-brains'
Researchers at Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health have demonstrated the use of stem-cell-derived "mini-brains" to detect harmful side effects of a common drug on the developing brain. Mini-brains are miniature human brain models, developed with human stem cells and barely visible to the human eye, whose cellular mechanisms mimic those of the developing human brain.
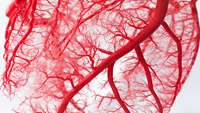
Blood vessels communicate with sensory neurons to decide their fate
Researchers at Pompeu Fabra University have shown for the first time that blood vessels communicate with neurons in the peripheral nervous system, regulating their proliferation and differentiation.
Treatment shows promise in treating deadly brain cancer
Researchers of McMaster University and the University of Toronto have developed a promising immunotherapy treatment for a deadly form of adult brain cancer called glioblastoma.