Synthego's CRISPR platform enables faster ID of potential Coronavirus treatment
Synthego, the genome engineering company, has collaborated with The Krogan Lab, a world-renowned scientific research unit at the Quantitative Biosciences Institute (QBI) at the University of California, San Francisco (UCSF), to deliver multiple CRISPR-based engineered cell lines to accelerate the study of potential treatment targets for SARS-CoV-2, the novel coronavirus that causes COVID-19 disease.
Stealthy microrobots that can evade the immune system
Microrobots have the potential to radically change the future of medicine. Their small bodies and ever-increasing capabilities allow them to navigate complex, confined environments inside our bodies to deliver therapeutics to sensitive, hard-to-reach places. They could mitigate the need for open surgery and minimize the side effects of treatments such as chemotherapy by delivering drugs to specific locations.
New electronic skin can react to pain like human skin
Researchers have developed electronic artificial skin that reacts to pain just like real skin, opening the way to better prosthetics, smarter robotics and non-invasive alternatives to skin grafts.
Cellulose wound dressing uses peptides to kill bacteria
Although it's vitally important to keep wounds free of harmful bacteria, antibacterial ointments have to be regularly reapplied, requiring bandages to be removed. A new wound dressing, however, is claimed to continuously kill bacteria all on its own.
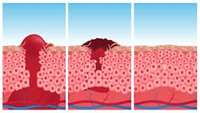
Activation of TRPA1 nociceptor promotes systemic adult mammalian skin regeneration
Adult mammalian wounds, with rare exception, heal with fibrotic scars that severely disrupt tissue architecture and function. Regenerative medicine seeks methods to avoid scar formation and restore the original tissue structures.
Silk scaffolds and magnetism to generate bone tissue and be able to use it in implants
The journal Materialia has recently published the outcome of a piece of research conducted by a group of researchers comprising several from the Department of Physical Chemistry at the UPV-EHU's Faculty of Science and Technology and BCMaterials, and others from centres at the University of Minho (Portugal).
Next-Gen Organoids Grow and Function Like Real Tissues
Organoids are fast-becoming one of the most cutting-edge tools of modern life sciences. The idea is to use stem cells to build miniature tissues and organs that accurately resemble and behave like their real counterparts.
Nobel Prize in Chemistry Awarded to 2 Scientists for Work on Genome Editing
Emmanuelle Charpentier and Jennifer A. Doudna developed the Crispr tool, which can alter the DNA of animals, plants and microorganisms with high precision.
Researchers develop new mouse model for SARS-CoV-2
Animal models that recapitulate SARS-CoV-2 infection and disease are urgently needed to help researchers understand the virus, develop therapies, and identify potential vaccine candidates.
Getting gene therapy to the brain
lone genetic mutation can cause a life-changing disorder with effects on multiple body systems. Lysosomal storage diseases, for example, of which there are dozens, arise due to single mutations that affect production of critical enzymes required to metabolize large molecules in cells. These disorders affect multiple organs including, notably, the brain, causing intellectual disability of varying degrees.