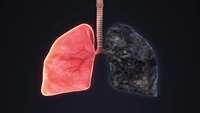
Stem cells from placental amniotic membrane slow lung scarring in pulmonary fibrosis
In a study released today in Stem Cells Translational Medicine (SCTM), a team led by researchers at the Eugenia Menni Research Centre (CREM) in Brescia, Italy, show for the first time how stem cells collected from human amniotic membrane (one of the two fetal membranes forming the amniotic sac, which surrounds the fetus during pregnancy and is generally discarded after a baby's birth) can slow the progression of scarring in pulmonary fibrosis. This pre-clinical study could lead to new treatments for this deadly disease.
Intranasal delivery of MSCs provides hope for treating Alzheimer's disease
In the search for a cure for Alzheimer's disease, mesenchymal stem cells and their derived extracellular vesicles (MSC-EVs) offer much promise, thanks to their protective and anti-inflammatory properties.
Researchers Find New Leukemia Genes using CRISPR Technology
Using the most advanced tools available, scientists discovered several novel genes not known to be involved in blood cancers, and used the powerful new data to paint a clearer map for how aggressive leukemia arises and grows, according to an article published in Nature Cancer.
'It's like you have a hand again': An ultra-precise mind-controlled prosthetic
In a major advance in mind-controlled prosthetics for amputees, University of Michigan researchers have tapped faint, latent signals from arm nerves and amplified them to enable real-time, intuitive, finger-level control of a robotic hand.
Experimental COVID-19 vaccine safe, generates immune response
An investigational vaccine, mRNA-1273, designed to protect against SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), was generally well tolerated and prompted neutralizing antibody activity in healthy adults, according to interim results published online today in The New England Journal of Medicine.
Adult astrocytes are key to learning and memory
Researchers at Baylor College of Medicine reveal that astrocytes, the most abundant cells in the brain, play a direct role in the regulation of neuronal circuits involved in learning and memory. The findings appear in the journal Neuron.
COPD as a lung stem cell disease: Single cell cloning tells the story of abnormal cells
Two internationally renowned stem cell experts have found an abundance of abnormal stem cells in the lungs of patients who suffer from Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD), a leading cause of death worldwide.
Controlling CAR T cells with light selectively annihilates skin tumors in mice
Bioengineers at the University of California San Diego have developed a control system that could make CAR T-cell therapy safer and more powerful when treating cancer. By programming CAR T cells to switch on when exposed to blue light, the researchers controlled the cells to destroy skin tumors in mice without harming healthy tissue.
New CAR-T target yields promising results for multiple myeloma
Too many patients with cancers like multiple myeloma relapse after treatment. This grim reality motivated researchers at Huntsman Cancer Institute (HCI) at the University of Utah (U of U) to try to improve the depth and durability of treatment response in multiple myeloma through a new cancer cell targeting mechanism.
Researchers cultivate mini lungs for SARS-CoV-2 research
A Bochum-based team intends to use organoids from stem cells to study the progression of SARS-CoV-2 infection and to identify antiviral substances.