Magnetic guidance improves stem cells' ability to treat occupational lung disease
Results of a study released today in Stem Cells Translational Medicine (SCTM) may point the way to a cure for a serious lung disease called silicosis that affects millions of workers worldwide. Silicosis results from years of breathing in dust microparticles of silica by workers in professions such as construction and sand blasting.
New insights into wound healing
The team, led by Delaram Shakiba, a postdoctoral fellow from the NSF Science and Technology Center for Engineering Mechanobiology (CEMB) at the McKelvey School of Engineering, discovered the way fibroblasts, or common cells in connective tissue, interact with the extracellular matrix, which provides structural support as well as biochemical and biomechanical cues to cells.
Transforming spleens into liver-like organs in mice
A team of researchers affiliated with several institutions in China has developed a means for coaxing a mouse spleen into behaving like a liver—a possible alternative to transplantation. In their paper published in the journal Science Advances, the group describes their technique and how well it worked with test mice.
Putting 'super' in natural killer cells
Using induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) and deleting a key gene, researchers at University of California San Diego School of Medicine have created natural killer cells -- a type of immune cell -- with measurably stronger activity against a form of leukemia, both in vivo and in vitro.
Jumping genes help make neurons in a dish
The process of making functional brain cells in a lab dish requires the precise activation of selfish genetic elements known as LINE-1 (L1) retrotransposons. The finding, from researchers at KAUST, could lead to safer and more effective regenerative therapies for Parkinson's disease and other brain conditions.
Process of stem cell autophagy may offer new targets for regenerative therapies
Researchers at Penn Medicine (PA, USA) have uncovered new roles of autophagy in embryonic stem cell renewal and differentiation. These processes, which pertain to chaperone-mediated autophagy (CMA) and a related metabolite, offer new insights that may be critical in the development of novel regenerative therapies. The study was recently published in Science.
FDA Approves CAR T-Cell Therapy for Adults With R/R Mantle Cell Lymphoma
FDA today approved the third chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy, this time granting a green light for Kite Pharma’s brexucabtagene autoleucel, the first cell-based gene therapy to treat relapsed or refractory mantle cell lymphoma (MCL).
Heart attack in a dish: a 3-D model
In the U.S., someone has a heart attack every 40 seconds, and yet researchers have not had a model that fully mimics what occurs in the human heart after a heart attack.
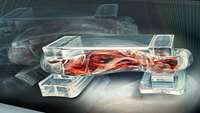
Research reveals insights into bioprinted skeletal muscle tissue models
Skeletal muscle can be functionally compromised by genetic myopathies, aging, traumatic injuries and tumor ablation. Under some conditions, such as severe traumatic injuries and volumetric muscle loss, the regeneration process is significantly hindered by fibrous scar tissue formation and therefore causing muscle dysfunction.
Cancer study may accidentally help researchers create usable blood stem cells
A massive research effort over more than a quarter century has tried to make personalized blood stem cells for use in treating leukemias, among many other uses.