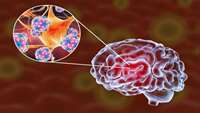
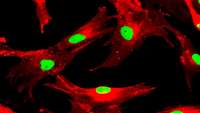
Scientists prove SARS-CoV-2 potential to infect human brain organoids
SARS-CoV-2 can infect human neural progenitor cells and brain organoids, as shown by researchers from the Shenzhen Institutes of Advanced Technology (SIAT) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences and their collaborators from The University of Hong Kong (HKU).
Controlled tissue regeneration with 3-D bioprinted spatiotemporally defined patterns of growth factors
A team of researchers in biomedical engineering, mechanical engineering and biomechanics in Ireland, the Netherlands and the U.S. recently developed 3-D bioprinted implants optimized with growth factors to facilitate angiogenesis—blood vessel growth from existing vasculature—and osteogenesis—new bone growth.
Putting 'super' in natural killer cells
Using induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) and deleting a key gene, researchers at University of California San Diego School of Medicine have created natural killer cells—a type of immune cell—with measurably stronger activity against a form of leukemia, both in vivo and in vitro.
'Self-eating' process of stem cells may be the key to new regenerative therapies
The self-eating process in embryonic stem cells known as chaperone-mediated autophagy (CMA) and a related metabolite may serve as promising new therapeutic targets to repair or regenerate damaged cells and organs, Penn Medicine researchers show in a new study published online in Science.
UCF researchers utilize Human-on-a-Chip® approach to model ALS pathology
A new study published today demonstrates that a technology developed at the University of Central Florida could serve as a more reliable clinically-based model of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) and a better screening tool for novel therapies than currently use preclinical models.
Researchers develop synthetic scaffolds to heal injured tendons and ligaments
Australia's love of sport means it has one of the highest rates of knee anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) injury and reconstruction in the world.
CD146 mesenchymal stem cells display greater therapeutic potential than CD146 cells for treating collagen-induced arthritis in mice
The characteristics and therapeutic potential of subtypes of mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) are largely unknown. In this study, CD146+ and CD146– MSCs were separated from human umbilical cords, and their effects on regulatory T cells (Tregs), Th17 cells, chondrogenesis, and osteogenesis were investigated.
Efficient Strategies for Microglia Replacement in the Central Nervous System
Microglia are important immune cells in the central nervous system (CNS). Dysfunctions of gene-deficient microglia contribute to the development and progression of multiple CNS diseases.
Stem cells from placental amniotic membrane slow lung scarring in pulmonary fibrosis
In a study released today in Stem Cells Translational Medicine (SCTM), a team led by researchers at the Eugenia Menni Research Centre (CREM) in Brescia, Italy, show for the first time how stem cells collected from human amniotic membrane (one of the two fetal membranes forming the amniotic sac, which surrounds the fetus during pregnancy and is generally discarded after a baby's birth) can slow the progression of scarring in pulmonary fibrosis.
Hungarian Scientist Wins €1 Million Prize For Groundbreaking Research That Could Eventually Restore Sight in Blindness
This year’s Körber Prize for European Science has gone to a Hungarian scientist whose revolutionary gene-editing treatment could cure a type of blindness that affects around one in 4,000 children.