Repetitive elements trigger RIG-I-like receptors to enhance hematopoietic stem cell formation
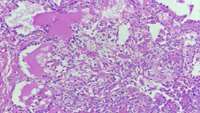
Hematopoietic stem cells can replenish all the different cell types of our blood system. For this reason, hematopoietic stem cells are the cells used in many blood diseases when patients need transplantations.
Non-hereditary mutation acts as natural gene therapy in patient with rare disease
Researchers affiliated with the Center for Cell-Based Therapy (CTC (ctcusp.org/rationale-2/presentation)) in Ribeirão Preto, Brazil, have identified for the first time a non-hereditary mutation in blood cells from a patient with GATA2 deficiency, a rare autosomal disease caused by inherited mutations in the gene that encodes GATA-binding protein 2 (GATA2). GATA2 regulates the expression of many genes that play a key role in developmental processes and cell renewal.
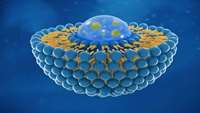
Researchers show safer, more targeted way to deliver CRISPR gene therapy
Light-activated liposomes could help to deliver CRISPR gene therapy—and the method could prove safer and more direct than current methods.
Children produce different antibodies in response to SARS-CoV-2
Children and adults produce different types and amounts of antibodies in response to infection with the new coronavirus, SARS-CoV-2, a new study from researchers at Columbia University Vagelos College of Physicians and Surgeons has found.
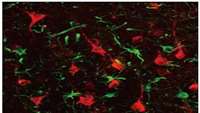
First non-human primate study showing promise of gene therapy for stroke repair
Stroke is a leading cause of death and severe long-term disability with limited treatments available. A research team led by Prof. Gong Chen at Jinan University, Guangzhou, China recently reported the first non-human primate study demonstrating successful in vivo neural regeneration from brain internal glial cells for stroke repair.
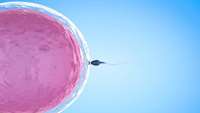
Preserving fertility in female cancer patients and ageing populations
A Monash University study has uncovered the role DNA repair plays in preserving egg quality, offering hope for women whose eggs may be damaged through treatments such as radiation and chemotherapy.
Further evidence shows clinical viability of natural tooth repair method
Over the last five years scientists at King's College London have been investigating a method of stimulating natural tooth repair by activating cells in the tooth to make new dentine. In a paper published today in the Journal of Dental Research, they have found further positive evidence that the method has the potential to be translated into a direct clinical approach.
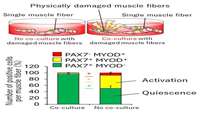
Damaged muscles don't just die, they regenerate themselves
Researchers building a model of muscle damage in a cultured system found that components leaking from broken muscle fibers activate ''satellite cells,'' which are muscle stem cells.
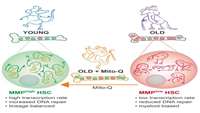
Novel approach identifies ‘young’ stem cells in old mice
In a collaborative study, researchers from Lund Stem Cell Center and University College London have developed a novel method of isolating ‘young’ stem cells still present in old mice.
Magnetic guidance improves stem cells' ability to treat occupational lung disease
Results of a study released today in Stem Cells Translational Medicine (SCTM) may point the way to a cure for a serious lung disease called silicosis that affects millions of workers worldwide.