How skin begins: New research could improve skin grafts, and more
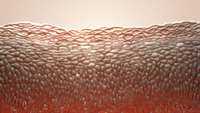
University of Colorado Boulder researchers have discovered a key mechanism by which skin begins to develop in embryos, shedding light on the genetic roots of birth defects like cleft palate and paving the way for development of more functional skin grafts for burn victims.
Study confirms role of brains support cells in Huntingtons, points to new therapies
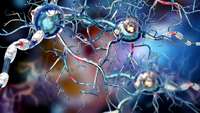
New research gives scientists a clearer picture of what is happening in the brains of people with Huntingtons disease and lays out a potential path for treatment.
Flipped cells cause blood vessels to leak in diabetes and other diseases
An enzyme activated in diabetics has been found to cause previously aligned cells in a blood vessel to reverse their orientation, creating misalignments that allow veins and arteries to leak three times more blood proteins than normally constructed blood vessels. Controlling the enzyme could ease symptoms of swelling, nerve pain, localized low blood pressure, and risk of infection in diabetes, other diseases that cause blood vessels to leak, and smoking.
Fat fuels aggressive brain cancers
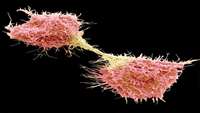
Fat is powering tumour growth in brain cancer, finds a new study by Cardiff University and the University of Florida.
Cancer stem cells use normal genes in abnormal ways
CDK1 is a "normal" protein—its presence drives cells through the cycle of replication. And MHC Class I molecules are "normal" as well—they present bits of proteins on the surfaces of cells for examination by the immune system.
Newly identified structure in lymph nodes was hiding in plain sight
In a study published this week in Nature Communications, scientists at Australias Garvan Institute of Medical Research have identified where the immune system remembers past infections and vaccinations—and where immune cells gather to mount a rapid response against an infection the body has seen before.
From gene-edited babies to male contraceptives: The most exciting medical innovations in 2018
It has been an exciting year for medical science, a field generally not known for giant revolutionary breakthroughs, but rather incremental discoveries that build on existing knowledge to improve our health and well being.
Virtual tumour new way to see cancer
Scientists in Cambridge have built a virtual reality (VR) 3D model of cancer, providing a new way to look at the disease.
New method grows brain cells from stem cells quickly and efficiently
Researchers at Lund University in Sweden have developed a faster method to generate functional astrocytes from embryonic stem cells. Astrocytes play a significant role in neurodegenerative diseases. The new method reduces the time required to produce the cells from months to two weeks, and the study has been published in Nature Methods.
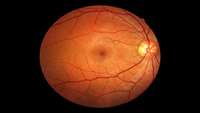
‘Retina in a dish’ provides new insight into inherited blindness
The inherited eye disease retinitis pigmentosa (RP) is caused by genetic changes that are not well understood. For example, mutations in cell proteins known as “splicing factors” can cause RP, though the exact mechanism behind the problem has been somewhat of a mystery.