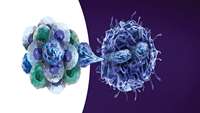
Gut intraepithelial T cells calibrate metabolism and accelerate cardiovascular disease
The biochemical response to food intake must be precisely regulated. Because ingested sugars and fats can feed into many anabolic and catabolic pathways1, how our bodies handle nutrients depends on strategically positioned metabolic sensors that link the intrinsic nutritional value of a meal with intermediary metabolism.
COMBINATION THERAPY TARGETS PANCREATIC CANCER STEM CELLS
A new drug combination tested in mice may target the cells responsible for driving some pancreatic tumors. The combination of gemcitabine and the experimental drug tigatuzumab eliminated populations of cancer stem cellsand reduced tumor growth in a mouse model of pancreatic cancer, researchers from the Johns Hopkins Sidney Kimmel Cancer Center reported at the AACR annual meeting.
Climate change will affect gender ratio among newborns, scientists say
Global warming will have a variety of effects on our planet, yet it may also directly impact our human biology, research suggests.
Study shows how stem cell injections helped dogs suffering from osteoarthritis
Researchers have developed what appears to be a simple, minimally invasive, effective way to treat osteoarthritis (OA) in dogs that may prove to be of considerable importance in treating humans, too. The study detailing this new approach appears in the latest issue of STEM CELLS Translational Medicine (SCTM).
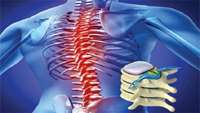
Regulators approve autologous stem cell therapy for spinal cord injury in Japanese first
An autologous mesenchymal stem cell (MSC)-based therapy for the treatment of spinal cord injury, developed by NIPRO Corporation (Osaka, Japan), has been conditionally approved for clinical treatment following a 13-patient trial. Stemirac, produced from bone marrow-derived MSCs, is believed to reduce inflammation and protect existing neurons, and should be administered within 40 days of injury.
Mini-placentas could provide a model for early pregnancy
Researchers say that new mini-placentas—a cellular model of the early stages of the placenta—could provide a window into early pregnancy and help transform our understanding of reproductive disorders. Details of this new research are published today in the journal Nature.
A study suggests that epigenetic treatments could trigger the development of aggressive tumours
A study headed by the Institute for Research in Biomedicine (IRB Barcelona) and published in the journal Nature Cell Biology examined whether the opening of chromatin (a complex formed by DNA bound to proteins) is the factor that determines the accumulation of more or fewer mutations in given regions.
First US patient in novel stem cell trial for stroke disability enrolled at UTHealth
The first U.S. patient to participate in a global study of a stem cell therapy injected directly into the brain to treat stroke disability was enrolled in the clinical trial this week at The University of Texas Health Science Center at Houston (UTHealth).
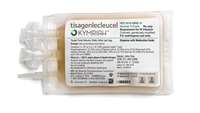
Kymriah gets NICE approval for DLBCL
Kymriah (tisagenlecleucel) - the only CAR-T cell therapy available for NHS patients in England and Wales for two distinct blood cancers - will be available on the NHS in England and Wales to eligible adults who did not respond to two or more previous treatments with DLBCL, with funding from the Cancer Drugs Fund (CDF).
Important signaling pathway in breast cancer revealed
Researchers at Kanazawa University report in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS) that a particular signaling pathway in breast cancer tumors causes cancer cells to divide symmetrically, expanding the tumor. Inhibiting the pathway with drugs could become a strategy for eliminating the cancer cells.