Untangling tau—researchers find a druggable target for treating Alzheimers disease
The accumulation of amyloid beta (Aβ) plaques and tangles of a protein called tau in the brain are hallmarks of Alzheimers disease (AD). Much effort has focused on the former, with many attempts made to prevent, slow or even reverse the presence of Aβ, and thus ameliorate the development of AD. To date, results have been mixed.
Sex-linked differences in cancer may identify gender-specific genetic drivers and predict responses to treatment
Analysis of male- and female-derived tumor samples revealed differences in prognostic biomarkers, genes that drive cancer, and in regulation of key pathways that may predict responses to treatment, according to results published in two studies in Cancer Research, a journal of the American Association for Cancer Research.
New stem cell technique may help fight cancer
T cells are cells of the immune system that fight infections, but also have the potential to eliminate cancer cells. Los Angeles: Scientists have developed a new technique to turn pluripotent stem cells which can give rise to every cell type in the body into mature T cells capable of killing tumours. The technique developed by researchers at the University of California, Los Angeles (UCLA) in the US uses structures called artificial thymic organoids, which work by mimicking the environment of the thymus, the organ in which T cells develop from blood stem cells.
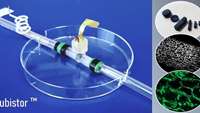
3D organ on a chip could accelerate search for new disease treatments
Researchers have developed a three-dimensional organ on a chip which enables real-time continuous monitoring of cells, and could be used to develop new treatments for disease while reducing the number of animals used in research.
Greater Benefits for Relapsing-Remitting MS Found with HSCT Therapy
Nonmyeloablative hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT) was associated with prolonged time to disease progression when compared to disease-modifying therapies (DMT) for patients with relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis (RRMS), according to results published in Journal of the American Medical Association (JAMA).
Study identifies an unexpected cell population key to blood cancer relapse
McMaster University researchers have provided evidence of new cancerous cells they have termed cancer regenerating cells, which are responsible for the return of acute myeloid leukemia after remission.
Energizing the immune system to eat cancer
Immune cells called macrophages are supposed to serve and protect, but cancer has found ways to put them to sleep. Now researchers at the Abramson Cancer Center of the University of Pennsylvania say theyve identified how to fuel macrophages with the energy needed to attack and eat cancer cells.
Novel hope for stem cell approach to treat diabetes
The team grew beta cells from human stem cells, but they made numerous changes to the "recipe" for producing insulin-producing beta cells.
Liver cancer patients can be treated for Hep C infection
A large, multi-center study refutes earlier suggestions that antiviral drugs for treating hepatitis C may lead to a higher recurrence of liver cancer.
Researchers reveal new mechanism to activate the immune system against cancer
A new mechanism for activating the immune system against cancer cells allows immune cells to detect and destroy cancer cells better than before, according to a study published this week in the journal Nature.