Treatment shown to improve the odds against bone marrow cancer
Hope has emerged for patients with a serious type of bone marrow cancer as new research into a therapeutic drug has revealed improved outcomes and survival rates.
Study identifies stem cell that gives rise to new bone and cartilage in humans
A decade-long effort led by Stanford University School of Medicine scientists has been rewarded with the identification of the human skeletal stem cell.
Stem Cells’ Consumption of ‘Sweets’ Helps Them Fight Inflammation
A new study published in STEM CELLS Translational Medicine shows that the energy metabolism of human mesenchymal stem cells (hMSCs) can be targeted to increase their ability to enhance tissue regeneration. The study offers a strategy that has immediate translational potential for improving hMSCs’ therapeutic success.
Engineers develop process to 3-D print cells to produce human tissue such as ligaments and tendons
With todays technology, we can 3-D-print sculptures, mechanical parts, prosthetics, even guns and food. But a team of University of Utah biomedical engineers have developed a method to 3-D-print cells to produce human tissue such as ligaments and tendons, a process that will greatly improve a patients recovery.
Researchers advance stem cell therapy with biodegradable scaffold
Rutgers scientists have created a tiny, biodegradable scaffold to transplant stem cells and deliver drugs, which may help treat Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s diseases, aging brain degeneration, spinal cord injuries and traumatic brain injuries.
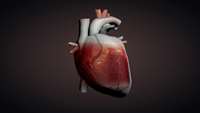
Scientists use stem cells to grow a BEATING human heart muscle for the first time ever
This development is a step forward in studying human physiology as it gives researchers a way to test treatments for conditions like heart failure on a lab-grown heart that can mimic a diseased adult one.
Japanese team creates human oogonia using human stem cells in artificial mouse ovaries
A team of researchers with members from several institutions in Japan has successfully generated human oogonia inside of artificial mouse ovaries using human stem cells. In their paper published in the journal Science, the group describes their work and their plans for the future.
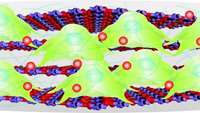
Researchers identify human skeletal stem cells
Human skeletal stem cells that become bone, cartilage, or stroma cells have been isolated from fetal and adult bones. This is the first time that skeletal stem cells, which had been observed in rodent models, have been identified in humans. The researchers were also able to derive the skeletal stem cells from human induced pluripotent stem cells, opening up new therapeutic possibilities. The discovery appears September 20 in the journal Cell.
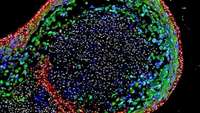
Scientists grow human esophagus in lab
This confocal microscopic image shows a two-month-old human esophageal organoid bioengineered by scientists from pluripotent stem cells. About 700 micrometers (0.027 inches) in size, the organoid is stained to visualize key structural …more
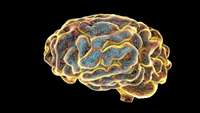
Creating custom brains from the ground up
Scientists studying how genetics impact brain disease have long sought a better experimental model. Cultures of genetically-modified cell lines can reveal some clues to how certain genes influence the development of psychiatric disorders and brain cancers. But such models cannot offer the true-to-form look at brain function that can be provided by genetically-modified mice.