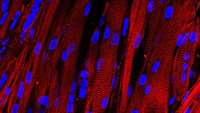
Diversity in the brain—how millions of neurons become unique
How is it possible that so many different and highly specific neuron types arise in the brain? A mathematical model developed by researchers from the University of Basels Biozentrum demonstrates that different variants of genes enable such a random diversity.
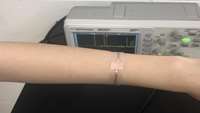
UW-Madison Researchers Develop Electric Bandage To Accelerate Healing
Bandages that promote quicker healing by harnessing the bodys own energy may sound like science fiction, but researchers at the University of Wisconsin-Madison have recently developed just that.
Researchers Regrow Hair on Wounded Skin
By stirring crosstalk among skin cells that form the roots of hair, researchers report they have regrown hair strands on damaged skin. The findings better explain why hair does not normally grow on wounded skin, and may help in the search for better drugs to restore hair growth, say the study’s authors.
Cells beneath the skin explain differences in healing
Differences in the cells that give skin its resilience and strength during wound repair may explain why individuals heal differently, according to a new Yale study published Nov. 23 in the journal Science.
Nobel laureates: Despite progress, cancer wont be wiped out
The winners of this years Nobel Prize for Medicine say they expect substantial advances toward treating cancer in the next several decades, although it is unlikely the disease could be eradicated.
Novartis says SMA gene therapy is cost-effective at $4-5 mln per patient
Swiss drugmaker Novartis, which is shifting into rare diseases, said on Monday it believes its new gene therapy for the deadly disease spinal muscular atrophy could be cost-effective to healthcare systems at $4 million to $5 million per patient.
Researchers develop tool to more easily detect cancer cells
Researchers at the University of Texas at Arlingtons College of Nursing and Health Innovation have developed a new nanoparticle-based platform for simultaneous imaging and treatment of esophageal cancer.
Viruses show new promise in treating cancer
Viruses have shown renewed promise in the treatment of cancer, after new research has shown they retain their cancer-killing ability even when injected into the bloodstream.
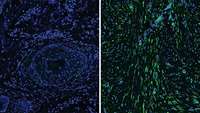
Muscle Satellite Cell Cross-Talk with a Vascular Niche Maintains Quiescence via VEGF and Notch Signaling.
Skeletal muscle is a complex tissue containing tissue resident muscle stem cells (satellite cells) (MuSCs) important for postnatal muscle growth and regeneration. Quantitative analysis of the biological function of MuSCs and the molecular pathways responsible for a potential juxtavascular niche for MuSCs is currently lacking.
Stem cells control their own fate, making lab-grown tissues less effective
Tissues grown in the lab from stem cells may fail to live up their therapeutic promise because the cells choose their own fate.



_117465.jpg)