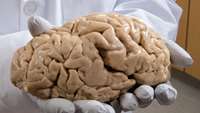
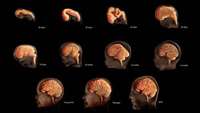
3-D tissue models provide unprecedented insight into human brain function and disease
Researchers have created 3-D tissue structures that recapitulate many aspects of specific human brain regions. These tiny, brain-region specific spheroids are allowing scientists to study previously inaccessible aspects of human brain development and function.
Electrospun manuka honey nanofibrous wound dressings
As instances of antibiotic resistance increase in the medical field, scientists are reexamining natural materials for their potential use in medicine. Honey has been used for thousands of years—from the time of Pharaohs—for their effectiveness in treating wounds and burns.
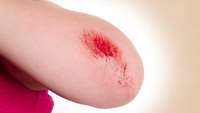
How signalling proteins result wound healing
What do a scraped knee, a paper cut, or any form of surgery have in common? The short answer is a wound in need of healing—but the long answer lies in a series of biological activities that allow tissues to repair themselves.
Development in production of retinal cells for treating blindness
Researchers at Karolinska Institutet and St Erik Eye Hospital in Sweden have discovered a way to refine the production of retinal cells from embryonic stem cells for treating blindness in the elderly.
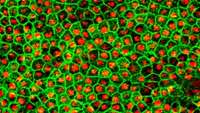
Stem cells and nerves interact in tissue regeneration and cancer progression
Stem cells can generate a variety of specific tissues and are increasingly used for clinical applications such as the replacement of bone or cartilage.
Hydrogel could be step forward in therapies to generate bones in head and neck
A team of UCLA School of Dentistry researchers has developed the first adhesive hydrogel specifically to regenerate bone and tissue defects following head and neck surgeries. Their invention was inspired in part by the way that marine mussels can stick to wet surfaces.
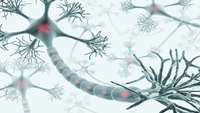
Stem cells exert tight control over the timing of brain development
Neural stem cells affect the timing and trajectory of division in brain development more than previously thought, RIKEN researchers have found1. This discovery could have important implications for our understanding of the evolution of the mammalian brain.
Further evidence shows clinical viability of natural tooth repair method
Over the last five years scientists at King's College London have been investigating a method of stimulating natural tooth repair by activating cells in the tooth to make new dentine. In a paper published today in the Journal of Dental Research, they have found further positive evidence that the method has the potential to be translated into a direct clinical approach.
Cellenkos® Inc. Announces FDA Clearance to Initiate Phase 1 Double- Blinded, Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Trial of Cryopreserved Cord Blood-Derived T-Regulatory Cells (CK0802) for Treatment of COVID-19 Associated Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome
Cellenkos Inc., a privately held, clinical stage biotech company announced today that the US Food & Drug Administration (FDA) has cleared the way to initiate a Phase 1 clinical trial of CK0802 (Cryopreserved Cord Blood Derived T-Regulatory Cells) for treatment of COVID-19 associated acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS).
A direct protein-to-protein binding couples cell survival to cell proliferation
Human cells respond to stresses like DNA damage, metabolic imbalance and starvation by first trying to repair the problem. If that does not work, the cells then induce programmed cell death, called apoptosis. Apoptosis is a highly regulated cell fate decision that removes about 50 billion to 70 billion cells each day in adults.