A light-activated remote control for cells
Complex signaling pathways coordinate cellular activities such as movement, proliferation and even death. For example, when signaling molecules bind to proteins called receptor tyrosine kinases on a cells surface, they trigger the receptors to form pairs and phosphorylate each other
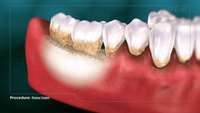
Periodontal Regeneration by Allogeneic Transplantation of Adipose Tissue Derived Multi-Lineage Progenitor Stem Cells in vivo
The ultimate goal of periodontal disease treatment is the reorganization of functional tissue that can regenerate lost periodontal tissue. Regeneration of periodontal tissues is clinically possible by using autogenic transplantation of MSCs.
3-D mini-gut model reflects autoimmune response to gluten in celiac patient tissue
In pursuit of a novel tool for the research and treatment of celiac disease, scientists at the Mucosal Immunology and Biology Research Center (MIBRC) at Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH) have validated the use of intestinal organoids.
New approach to drug discovery could lead to personalized treatment of neuropsychiatric disorders
Researchers have developed a method that could drastically accelerate the search for new drugs to treat mental health disorders such as schizophrenia.
Eggshells linked to bone growth
University of Massachusetts Lowell researches say they have discovered a use for eggs that goes far beyond simple cooking and eating.
Immune find could aid stem cell therapy quest
A discovery of how stem cells are protected from viruses could inform the development of therapies for use in medicine, research suggests.
Stem cell scientists clear another hurdle in creating transplant arteries
Scientists at the Morgridge Institute for Research are working toward a dream of creating artery banks similar to blood banks common today with readily-available material to replace diseased arteries during surgery.
Awakening stem cells to unlock the brains regenerative potential
The human body has powerful healing abilities. But treating brain disorders is no easy task, as brain cells—neurons—have limited ability to regenerate. Nonetheless, stem cells are a form of natural backup, a vestige of our days as still-developing embryos.
Scientists grow precursors for human pigment cells
Our hair, skin and eyes are colored by a pigment called melanin, which is produced by pigment cells called melanocytes.
Stem cells provide information about neuron resilience in ALS
Researchers at Karolinska Institutet in Sweden have developed a stem cell-based model to study the resilience and vulnerability of neurons in the neurodegenerative disease ALS. The results are published in the journal Stem Cell Reports, and could aid in the identification of new genetic targets for treatments protecting sensitive neurons.



_134246.jpg)