Finding suggests ways to promote adult heart tissue regeneration
Injured hearts do not heal themselves. Heart muscle cells, or cardiomyocytes, do not proliferate as much as necessary to replace dead tissue with new, pumping cells
Metabolic Switch Supports Human Mesenchymal Stem Cell Immunosuppression
The overarching importance of the immunomodulatory capacity of human mesenchymal stem cells (hMSCs) to their therapeutic output supposes a need to fully understand the regulatory mechanisms behind this ability in order to further develop hMSC-based therapies that can translate to the clinic.
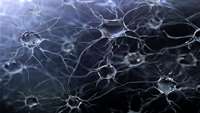
Calcium is key to age-related memory loss
The answer lies in synapses, the electrochemical connections between neurons that use neurotransmitter molecules to create the web of functions within the central nervous system. Professor Nick Hartell looked at whether calcium levels in the hippocampus, part of the brain necessary for learning and memory, might play a part.
Assembly of Human Stem Cell-Derived Cortical Spheroids and Vascular Spheroids to Model 3-D Brain-like Tissues
Human cerebral organoids derived from induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) provide novel tools for recapitulating the cytoarchitecture of human brain and for studying biological mechanisms of neurological disorders.
New mechanism of bone growth discovered
In a paper published in the journal Nature, an international research team led by researchers at Karolinska Institutet in Sweden reports that bone growth in mice takes place in accordance with the same principles as when new cells are produced in blood, skin and other tissue.
Transplanted bone marrow endothelial progenitor cells delay ALS disease progression
Transplantation of human bone marrow-derived endothelial progenitor cells (EPCs) into mice mimicking symptoms of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) helped more motor neurons survive and slowed disease progression by repairing damage to the blood-spinal cord barrier (BSCB), University of South Florida researchers report.
Impaired Bone Regenerative Effect of Exosomes Derived from Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells in Type 1 Diabetes
Stem cell‐derived exosomes have exhibited promise for applications in tissue regeneration. However, one major problem for stem cell‐derived exosome therapies is identifying appropriate source cells.
Targeting key gene could help lead to Down syndrome treatment
Using stem cells that can turn into other cells in the brain, researchers developed two experimental models a living 3D "organoid" model of the brain and a mouse brain model with implanted human cells to investigate early brain development linked to Down syndrome, according to the study in the journal Cell Stem Cell. The study focused on human chromosome 21 gene OLIG2.
Cancer cells are quick-change artists adapting to their environment
Until now, researchers have assumed that the growth of solid tumors originates from cancer stem cells characterized by specific surface markers, which develop in a fixed, hierarchical order. Accordingly, such cancer stem cells are responsible for tumor progression and produce specific types of more differentiated cancer cells whose fates are predetermined.
Study reveals large molecular differences between stem cells grown on different biomaterials
The genes necessary for the growth and survival of stem cells are influenced by the biomaterials on which theyre cultured, researchers at the University of Toronto have found.



_135335.jpg)