STEM CELLS STUDY AIMS TO FORESEE SCHIZOPHRENIA
Using new stem cell technology, scientists at the Salk Institute have shown that neurons generated from the skin cells of people with schizophrenia behave strangely in early developmental stages, providing a hint as to ways to detect and potentially treat the disease early (…)
Spinal organoids mimic neurodegenerative disease
Organoids that mimic the developing spinal cord could assist research and drug development for neurodegenerative diseases such as spinal muscular atrophy and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis.
Osteoblastic cell stimulation by pulsed electromagnetic fields
Bone fracture healing can be augmented with the application of pulsed electromagnetic fields (PEMFs), but a consensus regarding idealized conditions is lacking.
Cultured stem cells reconstruct sensory nerve and tissue structure in the nose
A team of researchers at Tufts University School of Medicine developed a method to grow and maintain olfactory stem cells in culture, which can then be used to restore tissue in the nose.
Research reveals insulin-producing beta cells may change function in diabetes
A revolutionary new study using only materials derived from humans has revealed that insulin-producing beta cells can change their function in diabetes - and that this change may be reversible.
Chemical pollutants in the home degrade fertility in both men and dogs, study finds
New research by scientists at the University of Nottingham suggests that environmental contaminants found in the home and diet have the same adverse effects on male fertility in both humans and in domestic dogs.
An enzymatic pathway in the human gut microbiome that converts A to universal O type blood
Access to efficient enzymes that can convert A and B type red blood cells to ‘universal’ donor O would greatly increase the supply of blood for transfusions.
Cerebral organoids at the air-liquid interface generate nerve tracts with functional output
Cerebral organoids, also sometimes called mini-brains or brain organoids, have become an important and useful tool in understanding human brain development and disease.
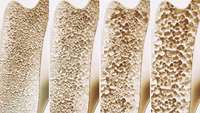
Research implicates causative genes in osteoporosis, suggesting new targets for future therapy
Scientists have harnessed powerful data analysis tools and three-dimensional studies of genomic geography to implicate new risk genes for osteoporosis, the chronic bone-weakening condition that affects millions of people. Knowing the causative genes may later open the door to more effective treatments.
Bluebird prices gene therapy at 1.58 million euros over 5 years
Bluebird bio Inc on Friday set a price for its gene therapy, Zynteglo, at 1.58 million euros ($1.78 million) over five years, after winning conditional approval in Europe this month to treat a rare genetic blood disorder.