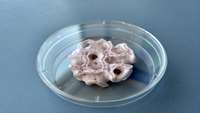
Astronauts could heal themselves with 3D-printed skin and bones
3D printing human tissue could help keep astronauts healthy all the way to Mars. An ESA project has produced its first bioprinted skin and bone samples.
Cryoprotectant-free cryopreservation of mammalian cells by superflash freezing
Cryopreservation is routinely used for the long-term storage of cells in various areas of academic, industrial, and clinical research.
Study reveals large molecular differences between stem cells grown on different biomaterials
The genes necessary for the growth and survival of stem cells are influenced by the biomaterials on which theyre cultured, researchers at the University of Toronto have found.
Proteins stand up to nerve cell regression
A study by Duke-NUS Medical School has found that members of the multiprotein Integrator complex, known for its role in gene regulation, are crucial for healthy brain development in fruit flies. The findings have implications for further understanding and treating neurodevelopmental disorders in humans.
Startup packs all 16GB of Wikipedia onto DNA strands to demonstrate new storage tech
Computer storage technology has moved from wires with magnets to hard disks to 3D stacks of memory chips. But the next storage technology might use an approach as old as life on earth: DNA. Startup Catalog announced Friday its crammed all of the text of Wikipedias English-language version onto the same genetic molecules our own bodies use
DNA repair gene linked to male infertility
A key DNA repair gene known as X-ray repair cross-complementing group 1, or XRCC1, plays a vital role in maintaining genomic stability and is highly expressed in the early stages of sperm cell development (also known as spermatogenesis). To date, however, the exact mechanisms of XRCC1 have been unclear.
Artificial muscles run on glucose and oxygen, just like the real thing
Scientists at Linköping University have blurred the line between robot and organism by developing an artificial muscle that runs off of glucose and oxygen like its organic counterpart. Made of a special polymer, the new plastic muscles open the promise of implantable artificial muscles and micro-robots that can be powered like living organs.
Study reveals factors behind embryonic stem cell state
Embryonic stem cells (ESC) have the ability to self-renew, and, being pluripotent have the potential to create almost any cell type in the body. The embryonic stem cell state is established and maintained by multiple regulatory networks that include epigenetic regulators; the function of these epigenetic regulators though has not been well-defined.
Nerve transfer surgery restores hand function and elbow extension in 13 young adults with complete paralysis
13 young adults with tetraplegia are able to feed themselves, hold a drink, brush their teeth, and write as a result of a novel surgical technique which connects functioning nerves with injured nerves to restore power in paralysed muscles Nerve transfer surgery has enabled 13 young adults with complete paralysis to regain movement and function in their elbows and hands, according to the largest case series of this technique in people with tetraplegia (paralysis of both the upper and lower limbs), published in The Lancet.
Boosting muscle stem cells to treat muscular dystrophy and aging muscles
Lying within our muscles are stem cells, invisible engines that drive the tissues growth and repair. Understanding the signal(s) that direct muscle stem cells to spring into action could uncover new ways to promote muscle growth. However, these mechanisms are poorly understood.