CRISPR to make IPS cells
Since 2006-2007 when mouse and human reprogramming were first reported, many different methods have been explored to make induced pluripotent stem (IPS) cells. Along the way we’ve all learned quite a lot about how pluripotency is regulated, whether it is in the context of maintenance or induction of this unique stem cell state.
Blood vessel-on-a-chips show anti-cancer drug effects in human cells
Researchers at the Institute of Industrial Science (IIS), the University of Tokyo, CNRS and INSERM, report a new organ-on-a-chip technology for the study of blood vessel formation and drugs targeting this event.
Human Embryonic Stem Cells for Ischemic LV Dysfunction
Is it feasible and safe to transplant cardiovascular progenitors derived from human embryonic stem cells (hESCs) to previously infarcted myocardium during coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG)?
A modified version of the CRISPR-Cas9 allows highly accurate gene editing
The scientific group from the Osaka University has developed the innovative method SNGD that can provide accurate editing of defective genes with less probability of error. CRISPR-Cas9 is the technology of genome editing, which is supposed to be used in the gene therapy of various hereditary diseases and cancer.
A new gene therapy transplantation technique could improve treatment of neurodegenerative diseases
Immune cells defending the central nervous system (the so-called microglia) have a key role in many neurodegenerative diseases.
Organ-on-chip technology enters next stage as experts test hepatitis B virus
Artificial human organs, or organ-on-chip technologies, simulate a whole organs cell make up and physiology. They act as alternatives to animal models in drug safety testing, but until now they have not been used to test how infectious diseases interact with the organs.
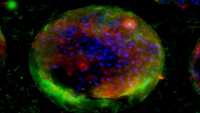
Scientists create functioning kidney tissue
The study led by Professors Sue Kimber and Adrian Woolf from The University of Manchester, signifies a significant milestone in the development of treatment for kidney disease.
Researchers engineer natural windpipe replacement alternative to synthetic scaffolding now being used
Biomedical engineers at Case Western Reserve University are growing tracheas by coaxing cells to form three distinct tissue types after assembling them into a tube structure-without relying on scaffolding strategies currently being investigated by other groups.
Two Types of CRISPR Gene Editing Could Be Useful in Treating Sickle Cell Anemia, Editas Reports
Two kinds of CRISPR gene editing therapies show promise as treatments for a number of blood diseases, including sickle cell anemia, Editas Medicine reports.
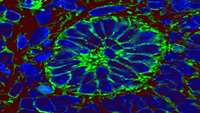
Scientists Create Most Sophisticated Human Liver Model Yet
Scientists at Wake Forest Institute for Regenerative Medicine (WFIRM) have developed the most sophisticated mini-livers to date. These organoids can potentially help scientists better understand certain congenital liver diseases as well as speed up efforts to create liver tissue in the lab for transplantation into patients.