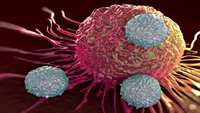
Sorrento Therapeutics Autologous Anti-CEA CAR-T Cell Therapy for Liver Metastases Demonstrates Therapeutic Activity in Stage IV Pancreas Cancer in a Phase 1b HITM-SURE Trial
Sorrento Therapeutics, Inc. (NASDAQ:SRNE) (“Sorrento”), cellular therapy focused subsidiary, TNK Therapeutics, Inc. (“TNK”), and Surefire Medical, Inc.
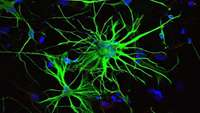
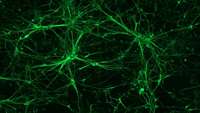
New cell model could lead to treatments for neurological diseases
Astrocytes are star shaped cells that are found in the brain and spine and were long thought to be the “glue” that binds nerve cells. However, recent advances show that they are in fact responsible for complex regulation of a variety of critical brain functions. They have also proven to be central to neurological diseases such as Alzheimer’s. But for research, these cells prove problematic.
Fragile X syndrome neurons can be restored
Fragile X syndrome is the most frequent cause of intellectual disability in males, affecting one out of every 3,600 boys born. The syndrome can also cause autistic traits, such as social and communication deficits, as well as attention problems and hyperactivity. Currently, there is no cure for this disorder.
Lab-grown Human Cerebellar Cells Yield Clues to Autism
Increasing evidence has linked autism spectrum disorder (ASD) with dysfunction of the brains cerebellum, but the details have been unclear. In a new study, researchers at Boston Childrens Hospital used stem cell technology to create cerebellar cells known as Purkinje cells from patients with tuberous sclerosis complex (TSC), a genetic syndrome that often includes ASD-like features. In the lab, the cells showed several characteristics that may help explain how ASD develops at the molecular level.
Stem-cell based stroke treatment repairs brain tissue
A team of researchers at the University of Georgia’s Regenerative Bioscience Center and ArunA Biomedical, a UGA startup company, have developed a new treatment for stroke that reduces brain damage and accelerates the brain’s natural healing tendencies in animal models. They published their findings in the journal Translational Stroke Research.
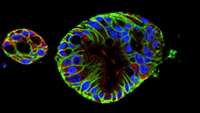
Scientists create intestine-derived organoids as a model to study necrotizing enterocolitis
Researchers have created novel multicellular models as a way to study necrotizing enterocolitis (NEC). The models, created with fetal and adult intestinal tissues, have already provided researchers with insights into fetal immune reactions to gut-colonizing bacteria.
New CRISPR Strategy Corrects Wider Range of Mutations Responsible for DMD
A new approach to CRISPR-Cas9 gene-editing technology, called myoediting, successfully restored dystrophin production and contraction force in heart muscle cells of Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD) patients.
Scientists culture human placenta stem cells for first time
In a milestone achievement for better understanding the development and function of the human placenta, scientists have derived and grown trophoblast stem cells for the first time.
Gene editing staves off deafness in mice
enome editing has been used to reduce hearing loss in ‘Beethoven’ mice, which carry a mutation that causes deafness in both mice and humans.
Researchers Use Human Neural Stem Cell Grafts to Repair Spinal Cord Injuries in Monkeys
Led by researchers at University of California San Diego School of Medicine, a diverse team of neuroscientists and surgeons successfully grafted human neural progenitor cells into rhesus monkeys with spinal cord injuries.