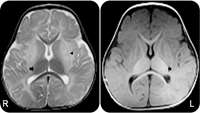
Sandhoff disease study shows proof of principle for gene therapy
Babies with the rare, deadly genetic disorder Sandhoff disease begin to miss developmental milestones just months after birth. Lacking muscle tone, they never learn to sit up, develop heads too large to lift and eventually suffer uncontrollable seizures. There is no cure
Gene therapy researchers find viral barcode to cross the blood-brain barrier
Gene therapies promise to revolutionize the treatment of many diseases, including neurological diseases such as ALS. But the small viruses that deliver therapeutic genes can have adverse side effects at high doses. UNC School of Medicine researchers have now found a structure on these viruses that makes them better at crossing from the bloodstream into the brain – a key factor for administering gene therapies at lower doses for treating brain and spinal disorders.
Adult endothelial stem cells can make fully functional blood vessels
The proper function of blood vessels is essential to life: blood vessels are responsible for transporting oxygen-rich red blood cells, nutrients, and immune cells throughout the body, to name just a few functions.
Bluebird Bio Presents Positive Early Results of Gene Therapy LentiGlobin for Sickle Cell Disease
Bluebird bio announced encouraging interim results from the ongoing Phase 1 clinical trial testing its investigational gene therapy LentiGlobin for patients with severe sickle cell disease (SCD).
Spare parts from small parts: novel scaffolds to grow muscle
RMIT biomedical engineers have successfully produced a 3D material that mimics nature to transform cells into muscle.
Chinese researchers report first lung stem cell transplantation clinical trial
A research team from Tongji University in China have made a breakthrough in human lung regeneration technology. For the first time, researchers have regenerated patients damaged lungs using autologous lung stem cell transplantation in a pilot clinical trial. The study can be found in the open access journal Protein & Cell which is published by Springer Nature and Higher Education Press.
$11.6 Million NIH Grant Supports Temple Researchers’ Exploration of New Cell-Free Stem Cell-Based Possibilities in Heart Repair
The incidence of heart disease is on the rise, and new therapeutic strategies are needed. Approaches based on stem cells, which can potentially preserve or even regenerate heart muscle cells damaged by ischemia – a hallmark of heart disease – are especially promising.
Scientists improve DNA transfer in gene therapy
Parkinsons disease, Huntingtons disease, cystic fibrosis these and many other fatal hereditary human diseases are genetically transmitted. Many cancers and cardiovascular diseases are also caused by genetic defects. Gene therapy is a promising possibility for the treatment of these diseases. With the help of genetically modified viruses, DNA is introduced into cells in order to repair or replace defective genes.
New-found stem cell helps regenerate lung tissue after acute injury
Researchers have identified a lung stem cell that repairs the organs gas exchange compartment, according to a new study from the Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania
Unlocking a cells potential to regenerate the heart
Some organisms have a remarkable capacity for regenerating tissue. If a fish or salamander suffers heart damage, for instance, their cells are able to divide and successfully repair the injured organ. Imagine if you could do the same.