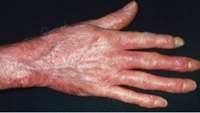
FDA Approves Talaris Therapeutics’ IND for its Allogeneic Cell Therapy FCR001 to be Evaluated in Patients with a Severe Form of Scleroderma
Talaris Therapeutics, Inc., a privately held biotechnology company developing transformative cell therapies that have the potential to induce durable immune tolerance across a range of indications, announced that the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has approved the company’s Investigational New Drug (IND) application for the evaluation of Talaris’ novel cell therapy FCR001 in the treatment of diffuse systemic sclerosis (SSc), a severe form of the rare autoimmune disease scleroderma.
Coronavirus detection using CRISPR-Cas13: Open-access SHERLOCK research protocol
The recent coronavirus (COVID-19) outbreak presents enormous challenges for global health. To aid the global effort, Broad Institute of MIT and Harvard, the McGovern Institute for Brain Research at MIT, and our partner institutions have committed to freely providing information that may be helpful, including by sharing information that may be able to support the development of potential diagnostics.
An organoid biobank for childhood kidney cancers that captures disease and tissue heterogeneity
Kidney tumours are among the most common solid tumours in children, comprising distinct subtypes differing in many aspects, including cell-of-origin, genetics, and pathology.
Tissue bioengineering product designated as orphan drug for butterfly skin
A tissue bioengineering product based on patient cells that have been corrected using genomic editing has been designated as an orphan drug by the European Medicines Agency (EMA) for the treatment of Recessive Dystrophic Epidermolysis Bullosa.
Novel method produces life-saving T cells from mesenchymal stromal cells
A new study released today in Stem Cells suggests for the first time that regulatory T-cells (Treg) induced by mesenchymal stromal cells can yield an abundant replacement for naturally occurring T-cells, which are vital in protecting the body from infection. Led by Rita I.
Feeling the Pressure: How Blood Vessels Sense Their Environment
Researchers from the University of Tsukuba identify the protein thrombospondin-1 as a novel extracellular mediator of mechanotransduction triggered by mechanical stress
Nature reveals there's more than one way to build a lung
Our bodies are home to hidden trees—complex, branching structures vital to the functions of organs including the lung, kidney, and pancreas.
Keratin scaffolds could advance regenerative medicine and tissue engineering for humans
Researchers at Mossakowski Medical Research Center of the Polish Academy of Science have developed a simple method for preparing 3-D keratin scaffold models which can be used to study the regeneration of tissue.
Researchers weave human tissue into new blood vessels
Researchers have used threads made of engineered human tissue to weave blood vessels that could one day help repair diseased or damaged blood vessels.
3-D tissue models provide unprecedented insight into human brain function and disease
Researchers have created 3-D tissue structures that recapitulate many aspects of specific human brain regions. These tiny, brain-region specific spheroids are allowing scientists to study previously inaccessible aspects of human brain development and function.