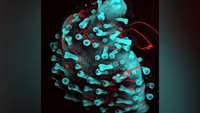
Lab-grown miniature human livers successfully transplanted in rats
Using skin cells from human volunteers, researchers at the University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine have created fully functional mini livers, which they then transplanted into rats.
Perspiration problems No sweat!
Solving sweat-related concerns that occur in daily life, such as hyperhidrosis and sweat smell, can improve people's quality of life. Now, researchers from Osaka University, in collaboration with Mandom Corporation, have succeeded in generating immortalized human eccrine sweat gland myoepithelial cells (iEM cells).
Researchers grow hairy skin from human stem cells
For more than 40 years, scientists and commercial companies have been recreating human skin in laboratories around the world. Yet all of these products lack important aspects of normal skin—hair, nerves, and fat.
A genomic biomarker that identifies human bone marrow‐derived mesenchymal stem cells with high scalability
Although the application of human mesenchymal stem cells (hMSCs) to repair damaged or diseased tissues has proven relatively effective, both the donor‐to‐donor variability in ex vivo expansion rates and the maintenance of stemness remain a bottleneck to widespread translation.
Standardizing organoid growth through controlled guidance systems
A recent innovation from an EPFL laboratory will enable, for the first time, mass production of standardized organoids. This breakthrough was achieved thanks to a customized guidance system that ensures homogenous cell culturing.
Early Data Demonstrate Strengths of Gene Therapy Approaches for Sanfilippo Syndrome
Initial safety and efficacy data from two clinical trials evaluating gene therapies for Sanfilippo syndrome were presented at the ASGCT 23rd Annual Meeting.
Preserving fertility in female cancer patients and ageing populations
A Monash University study has uncovered the role DNA repair plays in preserving egg quality, offering hope for women whose eggs may be damaged through treatments such as radiation and chemotherapy.
Stem cells from placental amniotic membrane slow lung scarring in pulmonary fibrosis
In a study released today in Stem Cells Translational Medicine (SCTM), a team led by researchers at the Eugenia Menni Research Centre (CREM) in Brescia, Italy, show for the first time how stem cells collected from human amniotic membrane (one of the two fetal membranes forming the amniotic sac, which surrounds the fetus during pregnancy and is generally discarded after a baby's birth) can slow the progression of scarring in pulmonary fibrosis. This pre-clinical study could lead to new treatments for this deadly disease.
Intranasal delivery of MSCs provides hope for treating Alzheimer's disease
In the search for a cure for Alzheimer's disease, mesenchymal stem cells and their derived extracellular vesicles (MSC-EVs) offer much promise, thanks to their protective and anti-inflammatory properties.
Researchers Find New Leukemia Genes using CRISPR Technology
Using the most advanced tools available, scientists discovered several novel genes not known to be involved in blood cancers, and used the powerful new data to paint a clearer map for how aggressive leukemia arises and grows, according to an article published in Nature Cancer.