Further evidence shows clinical viability of natural tooth repair method
Over the last five years scientists at King's College London have been investigating a method of stimulating natural tooth repair by activating cells in the tooth to make new dentine.
Gut Immune Cells May Help Send Multiple Sclerosis Into Remission
An international research team led by UC San Francisco scientists has shown, for the first time, that gut immune cells travel to the brain during multiple sclerosis (MS) flare-ups in patients. These gut cells seem to be playing a protective role, helping drive MS symptoms back into remission.
First non-human primate study showing promise of gene therapy for stroke repair
Stroke is a leading cause of death and severe long-term disability with limited treatments available. A research team led by Prof. Gong Chen at Jinan University, Guangzhou, China recently reported the first non-human primate study demonstrating successful in vivo neural regeneration from brain internal glial cells for stroke repair.
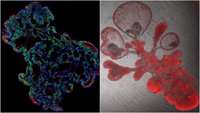
‘Mini-lungs’ reveal early stages of SARS-CoV-2 infection
To date, there have been more than 40 million cases of COVID-19 and almost 1.13 million deaths worldwide. The main target tissues of SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19, especially in patients that develop pneumonia, appear to be alveoli – tiny air sacs in the lungs that take up the oxygen we breathe and exchange it with carbon dioxide to exhale.
Researchers create human airway stem cells from patients' cells
For the first time, researchers have successfully created airway basal stem cells in vitro from induced pluripotent stem cells by reprogramming blood cells taken from patients.
New CRISPR technology helps revolutionize gene therapy
Researchers from the National Institutes of Health (MD, USA) and Harvard University (MA, USA) have used second-generation CRISPR gene-editing technology termed ‘base editing’ to revolutionize gene therapy in order to tackle a genetic disorder called Hutchinson–Gilford progeria syndrome (HGPS).
Synthetic biology and machine learning speed the creation of lab-grown livers
Researchers at the University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine have combined synthetic biology with a machine-learning algorithm to create human liver organoids with blood- and bile-handling systems. When implanted into mice with failing livers, the lab-grown replacement livers extended life.
Researchers identify gene responsible for cellular aging
Cellular reprogramming can reverse the aging that leads to a decline in the activities and functions of mesenchymal stem/stromal cells (MSCs). This is something that scientists have known for a while. But what they had not figured out is which molecular mechanisms are responsible for this reversal.
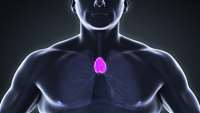
Scientists have built a fully functioning thymus from human cells
The thymus is the organ of the chest where T-lymphocytes mature, which play a vital role in the immune system. In an experimental study published in Nature Communications, the researchers reconstructed the thymus using stem cells taken from patients who had to have the organ removed during surgery.