Mesenchymal stem cell fate controlled by varying culture stiffness
Researchers from Tokyo Metropolitan University (Japan) have quantitatively characterized the heterogeneity in the responsiveness of mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) to the elastic modulus of culture substrates. The localization dynamics of YAP and RUNX2 proteins in cell nuclei and how this changed with stiffness, provides a basis to design the substrate elastic modulus to control the state of stem cells.
Effectiveness of CAR-T therapy could be indicated by presence of stem cell memory T cells
Having studied the effectiveness of CAR-T therapies in children with leukemia, researchers and clinicians at University College London (UCL) and Great Ormond Street Hospital (both London, UK) have discovered a subset of T cells that are likely to contribute to the success of the treatment.
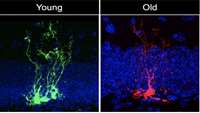
Study reveals neural stem cells age rapidly
In a new study published in Cell Stem Cell, a team led by USC Stem Cell scientist Michael Bonaguidi, Ph.D., demonstrates that neural stem cells—the stem cells of the nervous system—age rapidly.
Stem cells obtained from urine may be a strong iPSC source
A new study published in Scientific Reportsclaims to have isolated and characterized stem cells from human urine. The discovery, made by researchers from Heinrich Heine Universität Dusseldorf (Germany), would allow for the non-invasive collection of patient-specific stem cells that could be easily transformed into iPSCs or differentiated for regenerative therapies.
Safety of osteoarthritis cell therapy confirmed in new study
A team of researchers from the Center for Stem Cell and Regenerative Medicine (CSCRM) at Tokyo Medical and Dental University (Japan) has recently confirmed the safety of their novel stem cell therapy to treat knee pain caused by osteoarthritis.
Human–monkey chimeric embryos created using stem cells
Researchers in China and the USA have successfully grown chimeric embryos for up to 20 days by integrating human stem cells into primate embryos.
Gene therapy approach restores immune function to children with rare immunodeficiency disorder
Researchers from the University of California Los Angeles (UCLA; CA, USA) and Great Ormond Street Hospital (GOSH; London, UK) have collaborated to develop a new gene therapy for the treatment of severe combined immunodeficiency due to adenosine deaminase deficiency (ADA-SCID).
Mesenchymal stem cell treatment sees success in new muscular dystrophy study
Scientists at the Klara Medical Center (KMC; Czestochowa, Poland) have shown that mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) can be used for the treatment of muscular dystrophies – a group of progressive muscle diseases caused by a genetic mutation, resulting in muscle weakness.
Exosome spray helps with heart repair in rats after myocardial infarction
Despite the improvements made in modern surgical techniques, diagnostics and medications for myocardial infarction, many individuals still struggle with the long-term effects of tissue damage. Now, researchers have developed a minimally invasive exosome spray that helped repair rat hearts after myocardial infarction.