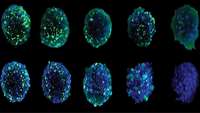
Researchers from Oxford and Bristol 3D print high-resolution tissue
At the University of Oxford, researchers have discovered a new way to 3D print living tissue with lab-grown cells. While there have been other successes of 3D printing tissue, such as in Sweden, this latest development in England could pave the way for regenerative medicine and enable the creation of complex tissues and cartilage.
Regenerative bandage accelerates healing in diabetic wounds
A simple scrape or sore might not cause alarm for most people. But for diabetic patients, an untreated scratch can turn into an open wound that could potentially lead to a limb amputation or even death.
A cure for blindness? Scientists manage to RESTORE sight in mice using GENE THERAPY
A team of US scientists from the National Institutes of Health used a gene injection to reprogramme dumb non-seeing retinal cells, and then use them to replace damaged light-sensitive rod cells.
Cultivating microtissues to replace animal testing
For the replacement of animal testing with alternatives in medical research, complex microtissues need to be cultivated. Researchers from Empa have developed a special polymer scaffold for three-dimensional cell cultures. Light beams act as signposts for the cells.
This matrix delivers healing stem cells to injured elderly muscles
A car accident leaves an aging patient with severe muscle injuries that wont heal. Treatment with muscle stem cells from a donor might restore damaged tissue, but doctors are unable to deliver them effectively. A new method may help change this.
Circulating Tumor Cells Get Sucked Up By Malaria Protein
Scientists in Copenhagen have developed a new tool for diagnosing and monitoring a wide variety of cancers, which uses a malaria protein known rVAR2 to grab hold of and remove circulating tumor cells (CTCs) from blood samples.
Probe illuminates Elusive Cancer Stem Cells in Live Mice
After a primary tumor is treated, cancer stem cells may still lurk in the body, ready to metastasize and cause a recurrence of the cancer in a form that’s more aggressive and resistant to treatment.
Repeated stimulation enlarges dendritic spines
Even in adult brains, new neurons are generated throughout a lifetime. In a publication in the scientific journal PNAS, a research group led by Goethe University describes plastic changes of adult-born neurons in the hippocampus, a critical region for learning: frequent nerve signals enlarge the spines on neuronal dendrites, which in turn enables contact with the existing neural network.
Researchers repair acute spinal cord injury in monkeys
Spinal cord injuries are among the most severe and difficult-to-treat medical conditions, usually resulting in permanent disability including loss of muscle function, sensation and autonomic functions.
Magnetic gene in fish may someday help those with epilepsy, Parkinsons
Michigan State University scientists are the first to discover a navigational gene in glass catfish called the electromagnetic-perceptive gene, or EPG, that responds to certain magnetic waves. Theyve already developed a way to use it to control movement in mice.