Europe’s first stem cell therapy backed by NICE
The National Institute for Health and Care Excellence has now published final guidelines backing Holoclar as an option to treat adults with moderate to severe limbal stem cell deficiency (LSCD) after eye burns.
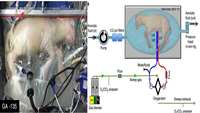
Premature lambs grown in a bag
Each year, about 15 million babies worldwide are born prematurely, of whom about 9% are extremely premature, born after fewer than 30 weeks of gestation. Research to develop an artificial womb in which to house extremely prema¬ture babies began in the 1960s, but no such device has yet been implemented.
iPS cell therapy reported safe
Japanese researchers reported this week that the first trial of induced pluripotent stem (iPS) cells in a human has proved safe and effective in halting the progression of age-related macular degeneration (AMD), though there was minimal improvement in vision.
Scientists create stem cell-based model of rare inherited neurological condition
An international team of scientists, led by University of California San Diego School of Medicine researchers, has created a human stem cell-based model of a rare, but devastating, inherited neurological autoimmune condition called Aicardi-Goutieres Syndrome (AGS).
Ohio State researchers develop regenerative medicine breakthrough
Researchers at The Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center and Ohio State’s College of Engineering have developed a new technology, Tissue Nanotransfection (TNT) that can generate any cell type of interest for treatment within the patient’s own body. This technology may be used to repair injured tissue or restore function of aging tissue, including organs, blood vessels and nerve cells
Scientists discover vitamin C regulates stem cell function, curbs leukemia development
Not much is known about stem cell metabolism, but a new study from the Childrens Medical Center Research Institute at UT Southwestern (CRI) has found that stem cells take up unusually high levels of vitamin C, which then regulates their function and suppresses the development of leukemia.
New discovery may impact treatment of autoimmune diseases
A new study has found a way of manipulating the differentiation of T cells in the immune system so as to strike a balance between pro-inflammatory and anti-inflammatory cells. This discovery may have implications for treating autoimmune diseases and some types of cancer.
Are Stem Cells the Link Between Bacteria and Cancer?
Gastric carcinoma is one of the most common causes of cancer-related deaths, primarily because most patients present at an advanced stage of the disease. The main cause of this cancer is the bacterium Helicobacter pylori, which chronically infects around half of all humans. However, unlike tumour viruses, bacteria do not deposit transforming genes in their host cells and how they are able to cause cancer has so far remained a mystery.
Cancer Immunotherapy: Whence and Whither
The current concepts and practice of cancer immunotherapy evolved from classical experiments that distinguished "self" from "non-self" and the finding that humoral immunity is complemented by cellular immunity.
Global standards for stem-cell research
Stem-cell research offers tremendous promise for biomedicine. It also raises vexing ethical and policy challenges. It can involve the destruction, creation and modification of human embryos, and has led to the premature marketing and use of unproven therapies.