Polycomb protein EED plays a starring role in hippocampal development
The dentate gyrus (DG) is the input region of the hippocampus and plays an important role in learning and memory. Although emerging evidence suggests that abnormal expression of the polycomb repressive complex 2 protein (PRC2) might cause neurological disease, the underlying molecular mechanisms had not been explored until recently.
Researchers report non-intrusive way to generate large quantities of stem cells from small amount of blood
A discovery by researchers at Queens University Belfast and Kings College London (KCL) could revolutionise treatment for vascular and diabetes related cardiovascular diseases.
No developmental differences in children conceived via assisted reproductive technology
Parents with children conceived via IVF, IUI or using infertility medication can rest assured that treatment has no impact on childhood development.
Studies Uncover New Approaches to Combat Hair Loss in Men and Women
Two recent studies highlight novel ways to combat pattern hair loss in men and women using small molecules such as JAK inhibitors that reawaken dormant hair follicles, as well as stem cell therapies aimed at growing new follicles.
Eye-in-a-dish model reveals genetic variants that may contribute to AMD
Age-related macular degeneration (AMD) is one of the most common causes of vision loss in people over age 65. The exact cause is unknown, but the fact that a family history of AMD increases a persons risk for the condition suggests genetics play an important role.
Frozen sperm retains its viability in outer space conditions
Zillionaires like Amazon founder Jeff Bezos who see the colonisation of space as an answer to the Earths ever threatened resources will be reassured to learn that human sperm retains its complete viability within the different gravitational conditions found in outer space.
Improving Tendon Healing with Proregenerative Educated Macrophages
As the natural tendon healing process fails to regenerate the composition and mechanical properties of native tissue, new strategies to improve healing are currently under development. Researchers from the laboratories of Ray Vanderby and Peiman Hematti (University of Wisconsin‐Madison, Madison, Wisconsin, USA) recently demonstrated that ligament injury led to an increase in proinflammatory M1 macrophages before scar formation and tissue compromise [1].
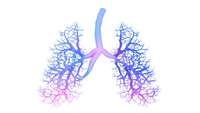
First lung map uncovers new insights into asthma
For the first time, researchers have mapped the building blocks of the human lungs and airways, in both asthma patients and normal people. The research from the Wellcome Sanger Institute, University Medical Center Groningen, Open Targets, GSK and collaborators revealed the identity of each cell type, creating the first draft Human Cell Atlas of the lung.
Embryo stem cells created from skin cells
As published in Cell Stem Cell, Dr. Yossi Buganim and his team discovered a set of genes capable of transforming murine skin cells into all three of the cell types that comprise the early embryo: the embryo itself, the placenta and the extra-embryonic tissues, such as the umbilical cord. In the future, it may be possible to create entire human embryos out of human skin cells, without the need for sperm or eggs.
Astronauts could heal themselves with 3D-printed skin and bones
3D printing human tissue could help keep astronauts healthy all the way to Mars. An ESA project has produced its first bioprinted skin and bone samples.