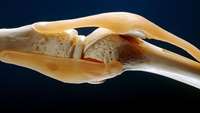
Bioactive scaffolds guide the way to sore knee relief, cartilage repair
NIBIB-funded researchers have developed a 3-D-printed scaffold coated in aggrecan, a native cartilage component, to improve the regeneration of cartilage tissue in joints.
A NOVEL TECHNOLOGY FOR GENOME-EDITING A BROAD RANGE OF MUTATIONS IN LIVE ORGANISMS
The ability to edit genes in living organisms offers the opportunity to treat a plethora of inherited diseases. However, many types of gene-editing tools are unable to target critical areas of DNA, and creating such a technology has been difficult as living tissue contains diverse types of cells.
Lung cell transplant boosts healing after the flu
The scientists found that transplanting a certain type of lung cell from healthy mice to those that had been injured by an infection with influenza could improve healing.
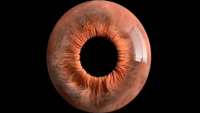
Shedding light on how the human eye perceives brightness
Japanese scientists are shedding new light on the importance of light-sensing cells in the retina that process visual information.
A new method of tooth repair? Scientists uncover mechanisms that could help future dental treatment
Stem cells hold the key to wound healing, as they develop into specialised cell types throughout the body – including in teeth.
Tomorrows bionic eyes will have Predator vision
Whether through illness or injury, 36 million people suffer from blindness worldwide, and until just a decade ago those afflicted had little chance of regaining their sight. In 2009, doctors at the University of Manchester implanted the first Argus II bionic eye in a patient. Now, 10 years later, the makers of the Argus II are trialing a more capable artificial-vision system one thats implanted directly into the patients brain.
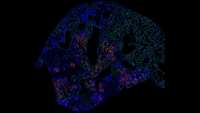
Development of a Chimeric Model to Study and Manipulate Human Microglia In Vivo
iPSC-derived microglia offer a powerful tool to study microglial homeostasis and disease-associated inflammatory responses. Yet, microglia are highly sensitive to their environment, exhibiting transcriptomic deficiencies when kept in isolation from the brain.
Scientists identify method to study resilience to pain
Scientists at the Yale School of Medicine and Veterans Affairs Connecticut Healthcare System have successfully demonstrated that it is possible to pinpoint genes that contribute to inter-individual differences in pain.
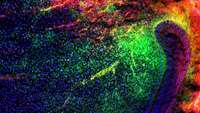
Discovery of the genetic conductor of brain stem cells
Our brain comprises 85 billion nerve cells and just as many so-called glial cells, which work in close contact with the former to guarantee their proper function.
FRESH 3D Printing Used to Rebuild Functional Components of the Human Heart
Scientists have taken a major step closer to being able to 3D bioprint functional organs, after researchers devised a method of rebuilding components of the human heart, according to a study published in the August 2nd edition of Science.