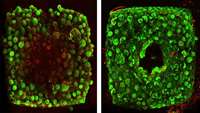
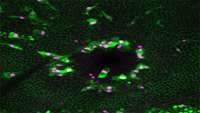
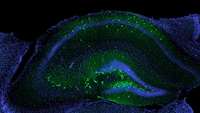
Sacrificial ink-writing technique allows 3D printing of large, vascularized human organ building blocks
20 people die every day waiting for an organ transplant in the United States, and while more than 30,000 transplants are now performed annually, there are over 113,000 patients currently on organ waitlists.
High-tech gel aids delivery of drugs
Drugs that help prevent the formation of unwanted or harmful proteins are currently being developed to treat a number of diseases, including cancer.
Accidental Discovery of New T-Cell Hailed as Major Breakthrough for ‘Universal’ Cancer Therapy
Researchers at Cardiff University have discovered a new type of killer T-cell that offers hope of a “one-size-fits-all” cancer therapy.
Scientists discover bodys protection shield
Scientists have discovered a way to manipulate the body’s own immune response to help boost tissue repair. The findings, published in Current Biology today [Monday 18 November], reveal a new network of protective factors to shield cells against damage.
New cell therapy improves memory and stops seizures following TBI
Researchers from the University of California, Irvine developed a breakthrough cell therapy to improve memory and prevent seizures in mice following traumatic brain injury. The study, titled "Transplanted interneurons improve memory precision after traumatic brain injury," was published today in Nature Communications.
Living skin can now be 3D-printed with blood vessels included
Researchers at Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute have developed a way to 3D print living skin, complete with blood vessels. The advancement, published online today in Tissue Engineering Part A, is a significant step toward creating grafts that are more like the skin our bodies produce naturally.
An artificial retina that could help restore sight to the blind
For more than a decade, researchers have been working to create artificial digital retinas that can be implanted in the eye to allow the blind to see again. Many challenges stand in the way, but researchers at Stanford University may have found the key to solving one of the most vexing: heat
First of a kind in-vitro 3D neural tissue model
Researchers at the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign have successfully used stem cells to engineer living biohybrid nerve tissue to develop 3D models of neural networks with the hopes of gaining a better understanding of how the brain and these networks work.
Three types of cells help the brain tell day from night
Bright light at night interrupts the bodys normal day-night cycles, called circadian rhythms, and can trigger insomnia. In fact, circadian rhythms play a major role in health. Disrupted day-night cycles have even been linked to increased incidence of diseases like cancer, heart disease, obesity, depressive disorders and type 2 diabetes in people who work night shifts. Therefore, understanding how human eyes sense light could lead to "smart" lights that can prevent depression, foster sleep at night, and maintain healthy circadian rhythms.
BRAIN’S ASTROCYTES PLAY STARRING ROLE IN LONG-TERM MEMORY
Star-shaped cells called astrocytes help the brain establish long-lasting memories, Salk researchers have discovered. The new work adds to a growing body of evidence that astrocytes, long considered to be merely supportive cells in the brain, may have more of a leading role.