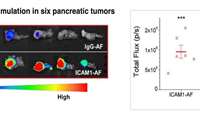
Precision chemo-immunotherapy for pancreatic cancer
Pancreatic cancer is highly lethal: according to the National Cancer Institute, only about 10 percent of patients remain alive five years after diagnosis. Now, a preclinical study from the lab of Marsha Moses, Ph.D. at Boston Children's Hospital, reports marked and lasting tumor regression in a mouse model, using a highly selective, potent, engineered antibody-drug combination.
Cancer treatment could be replicated for COVID-19
Beta-blockers could potentially be used to treat COVID-19, according to a new international study by Italian and Australian scientists.
Helping the immune system to combat cancer
Cancers sometimes escape our immune defenses because of the over-activity of molecular signaling systems, called checkpoint processes. Now we may be able to fight back using a new range of molecules, researchers in China report in theEuropean Journal of Medicinal Chemistry.
Artificial muscle sheets transform stem cells into bone
Specifically programmed materials can, under specific conditions, encourage stem cells to transform into bone cells—as revealed by a German research team under the leadership of the Helmholtz-Zentrum Geesthacht, Centre for Materials and Coastal Research.
Making blood on demand: How far have we come
The reconstitution of the blood system in humans holds great therapeutic potential to treat many disorders, like blood cancers, sickle-cell anemia and others.
Stem cells: New insights for future regenerative medicine approaches
Stem cells are considered one of the most promising tools in the field of regenerative medicine because they are a cell type that can give rise to all the cells in our bodies and that has the potential to be used to treat tissue loss due to damage or disease.
Scientists uncover proteins essential for memory B cell survival
Signals from two key proteins are essential for the survival of our 'immunological memory', according to new research from scientists at the Francis Crick Institute, published in theJournal of Experimental Medicine.
New drug candidate for the treatment of COVID-19
Researchers from the University of Kent, the Goethe-University in Frankfurt am Main (Germany), and the Hannover Medical School (Germany) have identified a drug with the potential to provide a treatment for COVID-19.
Researchers devise approach to treat rare, incurable form of blindness
Best vitelliform macular degeneration, or Best disease, is an inherited eye condition that typically leads to blindness over the course of a few decades. The disease can be caused by more than two hundred mutations in the BEST1 gene.