Studying the Neandertal DNA found in modern humans using stem cells and organoids
Protocols that allow the transformation of human induced pluripotent stem cell (iPSC) lines into organoids have changed the way scientists can study developmental processes and enable them to decipher the interplay between genes and tissue formation, particularly for organs where primary tissue is not available.
Protocols that allow the transformation of human induced pluripotent stem cell (iPSC) lines into organoids have changed the way scientists can study developmental processes and enable them to decipher the interplay between genes and tissue formation, particularly for organs where primary tissue is not available. Now, investigators are taking this technology and applying it to study the developmental effects of Neandertal DNA. The findings are reported June 18 in the journal Stem Cell Reports.
"Using iPSC lines to study the functions of archaic human DNA is an untapped but very interesting approach," says senior author J. Gray Camp of the Max Planck Institute for Evolutionary Anthropology in Germany and the University of Basel in Switzerland. "No one has ever been able to look at the role Neandertal DNA plays during development."
Studies have found that about 2% of the genomes of modern humans from outside Africa are composed of Neandertal DNA. This archaic DNA is a result of mating between the two groups tens of thousands of years ago.
In the new study, the team used resources from the Human Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells Initiative (HipSci), an international consortium that provides data and cell lines for research. Nearly all of the data and cell lines in HipSci are from people of UK and Northern European descent. The researchers analyzed this cell line resource for its Neandertal DNA content and annotated functional Neandertal variants for each of the cell lines.
"Some Neandertal alleles have relatively high frequency in this population," Camp explains. "Because of that, this iPSC resource contains certain genes that are homozygous for Neandertal alleles, including genes associated with skin and hair color that are highly prevalent in Europeans."
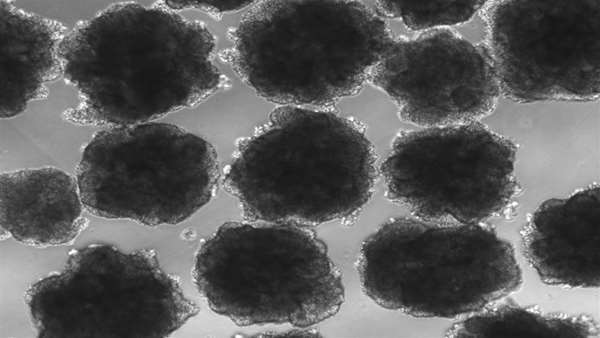
Camp's team used five cell lines to generate brain organoids and generated single-cell RNA sequencing data to analyze their cell composition. They showed that this transcriptomic data could be used to track Neandertal-derived RNA across developmental processes. "This is a proof-of-principal study showing that you can use these resources to study the activity of Neandertal DNA in a developmental process," Camp says. "The real challenge will be scaling up the number of lines in one experiment, but this is already starting to be possible."
Camp notes that this research could be expanded to study other ancient human populations, including Denisovans, which have genes that are present primarily in Oceanian populations. His team also plans to continue studying Neandertal alleles using HipSci and other resources. "Organoids can be used to study a number of different developmental processes and phenotypes controlled by Neandertal DNA, including the intestinal tract and digestion, cognition and neural function, and the immune response to pathogens," he concludes.
The researchers have generated a web browser with this information to make the data easily accessible for future research.
Reference:https://www.cell.com/stem-cell-reports/fulltext/S2213-6711(20)30190-9



ارسال به دوستان