Mapping cell types in the human body
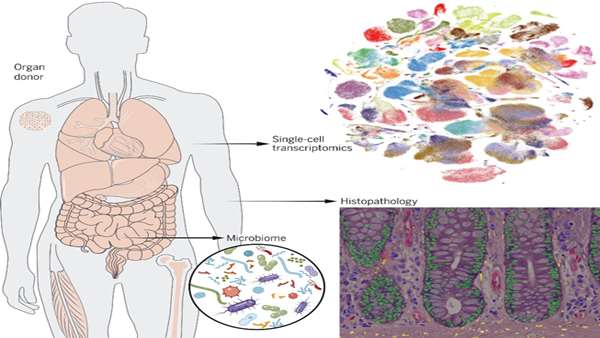
The Tabula Sapiens is a molecular reference atlas for more than 400 cell types of the human body. The Tabula Sapiens Consortium has used single-cell transcriptomics to measure the messenger RNA molecules in each of nearly 500,000 cells from 24 tissues and organs.
The Tabula Sapiens is a molecular reference atlas for more than 400 cell types of the human body. The Tabula Sapiens Consortium has used single-cell transcriptomics to measure the messenger RNA molecules in each of nearly 500,000 cells from 24 tissues and organs. These data enable new insights into how the human genome parts list is used to create distinct cell types within the human organism. In addition to creating a detailed molecular definition of these cell types, the atlas reveals many other aspects, including how the same gene can be spliced differently in different cell types, how shared cell types in different tissues can have subtle differences in their identities.
One current approaches to make cell atlases is that individual organs are often collected at different locations and donors, and processed using different protocols. Controlled comparisons of cell types between different tissues and organs are especially difficult when donors differ in genetic background, age, environmental exposure, and epigenetic effects. To address this, researchers developed an approach to analyzing large numbers of organs from the same individual. They collected multiple tissues from individual human donors and performed coordinated single-cell transcriptome analyses on live cells. The donors had come from a range of ethnicities, have been balanced by gender, have a mean age of 51 years, and have a variety of medical backgrounds.
The Tabula Sapiens also has provided an opportunity to densely and directly sample the human microbiome throughout the gastrointestinal tract.



ارسال به دوستان