Identification of essential genes for cancer immunotherapy
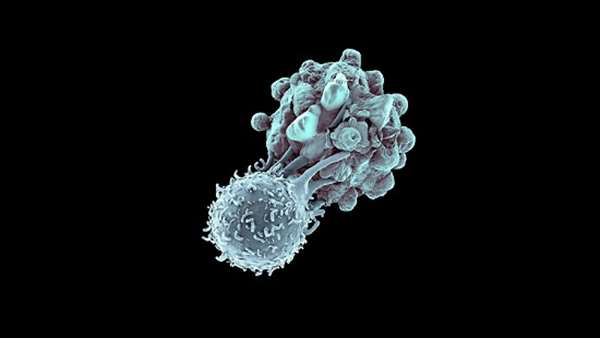
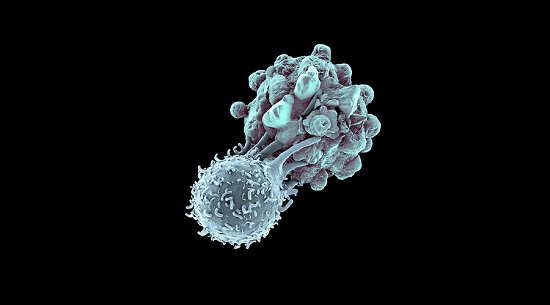
Somatic gene mutations can alter the vulnerability of cancer cells to T-cell-based immunotherapies. Here we perturbed genes in human melanoma cells to mimic loss-of-function mutations involved in resistance to these therapies, by using a genome-scale CRISPR–Cas9 library that consisted of around 123,000 single-guide RNAs, and profiled genes whose loss in tumour cells impaired the effector function of CD8+ T cells.
Somatic gene mutations can alter the vulnerability of cancer cells to T-cell-based immunotherapies. Here we perturbed genes in human melanoma cells to mimic loss-of-function mutations involved in resistance to these therapies, by using a genome-scale CRISPR–Cas9 library that consisted of around 123,000 single-guide RNAs, and profiled genes whose loss in tumour cells impaired the effector function of CD8+ T cells. The genes that were most enriched in the screen have key roles in antigen presentation and interferon-γ signalling, and correlate with cytolytic activity in patient tumours from The Cancer Genome Atlas. Among the genes validated using different cancer cell lines and antigens, we identified multiple loss-of-function mutations in APLNR, encoding the apelin receptor, in patient tumours that were refractory to immunotherapy. We show that APLNR interacts with JAK1, modulating interferon-γ responses in tumours, and that its functional loss reduces the efficacy of adoptive cell transfer and checkpoint blockade immunotherapies in mouse models. Our results link the loss of essential genes for the effector function of CD8+ T cells with the resistance or non-responsiveness of cancer to immunotherapies.
Reference: http://www.nature.com/nature/journal/v548/n7669/full/nature23477.html?foxtrotcallback=true



ارسال به دوستان