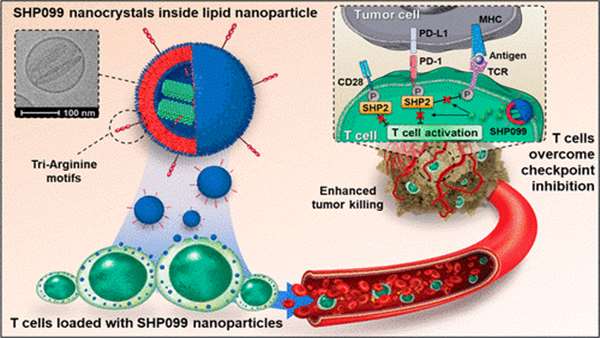
Whereas adoptive T cell therapy has been extensively studied for cancer treatment, limited primarily due to immune dysfunction related to poor cell engraftment, tumor infiltration and lack of a target. Researchers have presented a strategy to load T cells with SHP099, an allosteric SHP2 inhibitor, to enhance the therapeutic efficacy of the T cells.
Loading of SHP099 into lipid nanoparticles resulted in nanocrystal formation of SHP099 inside the lipid vesicles and allowed high loading efficiency and prolonged retention of SHP099 nanocrystals within T cells. Cell-loaded SHP099 enabled sustained inhibition of the PD-1/PD-L1 signaling and increased cytolytic activity of the T cells.
Researchers have showed in a mouse model that tumor-homing T cells can circulate with the cargos, improving their tumor accumulation compared to systemically administered lipid nanoparticles.
On an established solid tumor model, adoptively transferred SHP099 loaded T cells induced complete tumor eradication and durable immune memory against tumor rechallenging on all treated mice by effectively inhibiting the PD-1/PD-L1 checkpoint signal.
They demonstrated that the combination of T cell therapy with SHP2 inhibition is a promising therapeutic strategy, and the lipid nanocrystal platform could be generalized as a promising approach for T cell loading of immunomodulatory drugs.



ارسال به دوستان