AI-powered “patients-on-a-chip” could hold the future of drug development
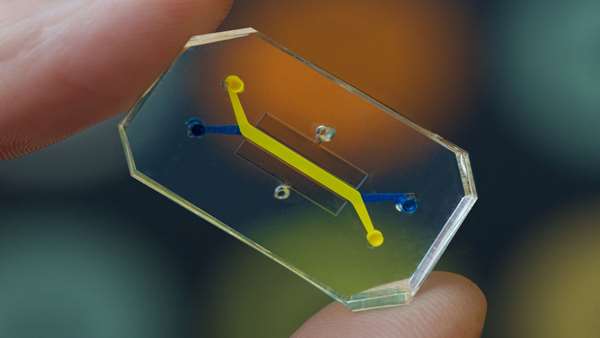
Heart-on-a-chip. Lung-on-a-chip. Brain-on-a-chip. You name the organ, scientists have likely found a way to recreate its tissues inside a small polymer rectangle, thanks to stem cells and some precise engineering.
Heart-on-a-chip. Lung-on-a-chip. Brain-on-a-chip. You name the organ, scientists have likely found a way to recreate its tissues inside a small polymer rectangle, thanks to stem cells and some precise engineering.
In 2020, researchers united these so-called “organs-on-chips” into a “patient-on-a-chip” to simulate the human body in miniature. This technology has opened the door to testing drugs on interconnected, living human tissues, which researchers say could help to streamline the costly and inefficient drug development process. Connect these different organ chips together, allowing fluid to transfer between them, and you have a patient-on-a-chip, also called a microphysiological system. “The level of clinical mimicry that we’re able to get nowadays is really kind of amazing,” says Harvard’s Ingber. In 2010, his lab pioneered a lung-on-a-chip, and in 2020, institute researchers combined multiple organ systems to form a whole “body” or “patient” on a chip. Because the chips contain living human tissues, experimenting on them can generate findings that are more relevant to humans than research on animals, Ingber says.
Recent advances have eased some of the challenges that previously stood in the way of the technology’s wide-scale adoption. One such challenge had been obtaining the living human cells that go inside the chips, wrote the editors of an organ-on-a-chip special issue of Stem Cell Reports in September. This has gotten easier as stem cells become more available and relatively affordable, allowing scientists to turn the general, non-specific cells of an individual into a specific lung or brain cell in the lab, Quris’ Bentwich says.
Whether or not they are widely adopted, these microscopic systems provide a literal window into the inner workings of human cells and tissues, Ingber says. And as they generate more and more data on the molecular impact of drugs on our bodies, he says, artificial intelligence will play an important role in turning that data into meaningful insights.
https://scienceline.org/2022/02/ai-powered-patients-on-a-chip/



ارسال به دوستان