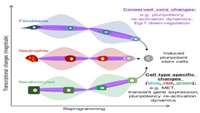
Cell Type of Origin Dictates the Route to Pluripotency
Our current understanding of induced pluripotent stem cell (iPSC) generation has almost entirely been shaped by studies performed on reprogramming fibroblasts.
Human Neural Stem Cell Transplantation Rescues Functional Deficits in R6/2 and Q140 Huntingtons Disease Mice
Huntingtons disease (HD) is an inherited neurodegenerative disorder with no disease-modifying treatment. Expansion of the glutamine-encoding repeat in the Huntingtin (HTT) gene causes broad effects that are a challenge for single treatment strategies.
Transplantation of iPS cell-derived neural progenitors overexpressing SDF-1α increases regeneration and functional recovery after ischemic stroke
Ischemic stroke is a leading cause of human death and disability while clinical treatments are limited. The adult brain possesses endogenous regenerative activities that may benefit tissue repair after stroke. Trophic factors such as stromal cell-derived factor 1 alpha (SDF-1α) are upregulated in the ischemic brain, which promote endogenous regeneration.
The Most Life-Changing Breakthroughs in Genetics of 2017
In a landmark decision made this past August, the Food and Drug Administration approved a treatment for childhood leukemia that works by genetically modifying a patient’s own blood cells to turn them into cancer killers. The FDA called it the first approved “gene therapy,” though experts quibbled over whether that term technically applies. Either way, it was a pretty big deal, and a decision that will pave the way for an era of FDA-sanctioned human gene modification.
Stem cells conduct cartilage regeneration but are not directly involved
Therapy with mesenchymal stem cells, the so-called progenitor cells of connective tissue, holds great promise for the regeneration of cartilage tissue but how stem cell therapy contributes to the healing of damaged connective tissue has been unclear.
Molecular and functional variation in iPSC-derived sensory neurons
Induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs), and cells derived from them, have become key tools for modeling biological processes, particularly in cell types that are difficult to obtain from living donors. Here we present a map of regulatory variants in iPSC-derived neurons, based on 123 differentiations of iPSCs to a sensory neuronal fate.
Organizing an Olympiad that promotes stem cell sciences and regenerative medicine in Iran
Secretary of the council for stem cell sciences and technologies pointing out that the first-stage winners of the 24th Olympiad of the Student testing Organization can participate in the first student Olympiad of Stem Cell sciences and tissue engineering.
Mini brains may wrinkle and fold just like ours
Flat brains growing on microscope slides may have revealed a new wrinkle in the story of how the brain folds.
3-D printed microfibers could provide structure for artificially grown body part
Much as a frame provides structural support for a house and the chassis provides strength and shape for a car, a team of Penn State engineers believe they have a way to create the structural framework for growing living tissue using an off-the-shelf 3-D printer.
T-Regulating Hair Follicle Stem Cells
Regulatory T (Treg) cells are key regulators of immune tolerance and are capable of suppressing multiple immune cell types and blocking excessive inflammatory responses. Although roles for tissue-resident Foxp3+ Treg cells in maintaining non-lymphoid tissue homeostasis have been suggested, evidence of a relationship between tissue-specific stem cells and Treg cells remains sparse