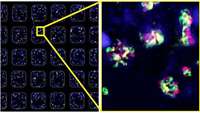
Cancer immunotherapy wins the 2018 medicine Nobel Prize
James P. Allison of MD Anderson Cancer Center in Houston and Tasuku Honjo of Kyoto University in Japan have won the Nobel Prize in physiology or medicine for advances in harnessing the immune system to fight cancer.
Single transplantation of therapeutic macrophages improves rare lung disease in mice
Hereditary pulmonary alveolar proteinosis (herPAP) is a rare disease characterized by the slow build-up of lipo-protein material in the lungs due to the failure of highly specialized cells called macrophages, which usually eat away this material from the pulmonary air-space.
Scientists create human esophagus in stem cell first
The esophagus is the muscular tube that moves the food and liquids we ingest from our throats all the way to our stomachs.
Gene editing technology may improve accuracy of predicting individuals heart disease risk
Scientists may now be able to predict whether carrying a specific genetic variant increases a persons risk for disease using gene editing and stem cell technologies, according to new research in the American Heart Associations journal Circulation.
STEM CELL RESEARCH HELPS TO IDENTIFY ORIGINS OF SCHIZOPHRENIA
New University at Buffalo research demonstrates how defects in an important neurological pathway in early development may be responsible for the onset of schizophrenia later in life.
Novartis signs Chinese manufacturing deal with Cellular Biomedicines for Kymriah
Swiss pharmaceutical company Novartis has signed an exclusive marketing agreement with Cellular Biomedicines to manufacture its CAR-T therapy Kymriah in China.
Autism linked to egg cells difficulty creating large proteins
New work from Carnegies Ethan Greenblatt and Allan Spradling reveals that the genetic factors underlying fragile X syndrome, and potentially other autism-related disorders, stem from defects in the cells ability to create unusually large protein structures. Their findings are published in Science.
Researchers transform human blood cells into functional neurons
Human immune cells in blood can be converted directly into functional neurons in the laboratory in about three weeks with the addition of just four proteins, researchers at the Stanford University School of Medicine have found.
Robots grow mini-organs from human stem cells
An automated system that uses robots has been designed to rapidly produce human mini-organs derived from stem cells. Researchers at the University of Washington School of Medicine in Seattle developed the new system.
UK panel rejects Kymriah for adults with lymphoma due to cost
An independent body that offers guidance to improve health and social care in England recommended against the use of tisagenlecleucel, a chimeric antigen receptor T-cell therapy, in adults with relapsed or refractory large B-cell lymphoma.