Biomedical engineers and medical researchers at UNSW Sydney have made discoveries about embryonic blood stem cell creation that could one day eliminate the need for blood stem cell donors.The achievements are part of a move in regenerative medicine towards the use of "induced pluripotent stem cells" to treat disease, where stem cells are reverse engineered from adult tissue cells rather than using live human or animal embryos.
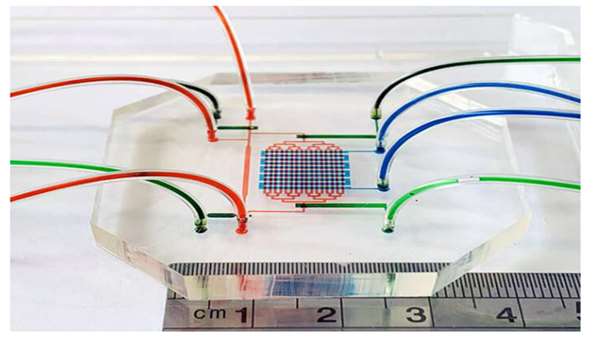
researchers from UNSW School of Biomedical Engineering demonstrated how a simulation of an embryo's beating heart using a microfluidic device in the lab led to the development of human blood stem cell "precursors,"which are stem cells on the verge of becoming blood stem cells.researchers from UNSW Medicine & Health revealed the identity of cells in mice embryos responsible for blood stem cell creation.Both studies are significant steps towards an understanding of how, when, where and which cells are involved in the creation of blood stem cells.In the future, this knowledge could be used to help cancer patients, among others, who have undergone high doses of radio- and chemotherapy, to replenish their depleted blood stem cells.
in the last few decades, biomedical engineers have been trying to make blood stem cells in laboratory dishes to solve the problem of donor blood stem cell shortages.Part of the problem is that we still don't fully understand all the processes going on in the microenvironment during embryonic development that leads to the creation of blood stem cells at about day 32 in the embryonic development. So researchers made a device mimicking the heart beating and the blood circulation. These systems promoted the development of precursor blood stem cells which can differentiate into various blood components—white blood cells, red blood cells, platelets and others. These systems promoted the development of precursor blood stem cells which can differentiate into various blood components—white blood cells, red blood cells, platelets and others.
They hope it could be a step towards solving challenges limiting regenerative medical treatments today: donor blood stem cell shortages, rejection of donor tissue cells, and the ethical issues surrounding the use of IVF embryos.
researchers are working on up-scaling manufacture of these cells using bioreactors.
The blood stem cell research that could change medicine of the future (phys.org)



ارسال به دوستان